Machine Theory of Mind for Autonomous Cyber-Defence
Paper and Code
Dec 05, 2024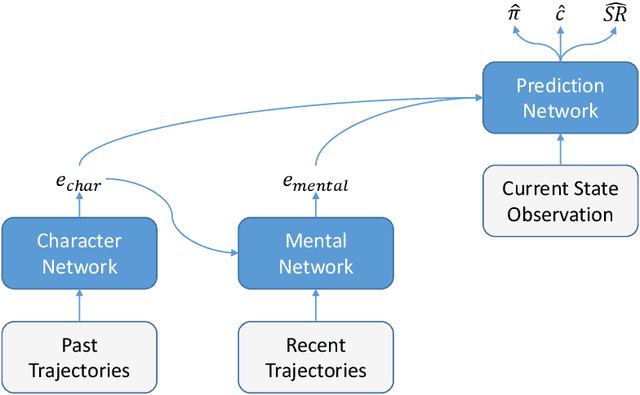
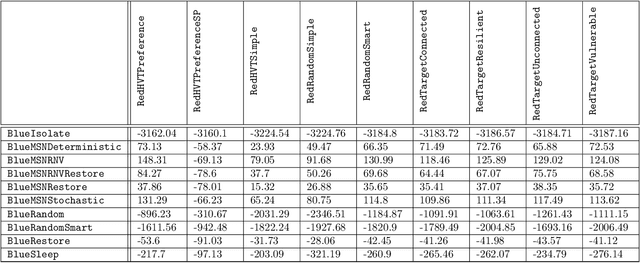
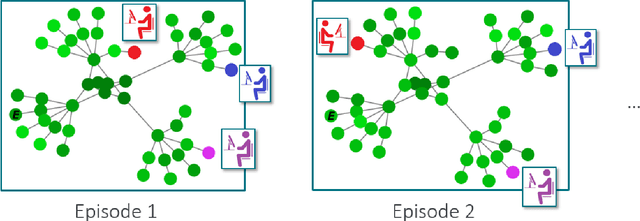
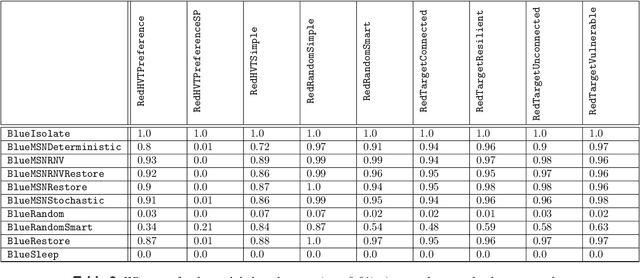
Intelligent autonomous agents hold much potential for the domain of cyber-security. However, due to many state-of-the-art approaches relying on uninterpretable black-box models, there is growing demand for methods that offer stakeholders clear and actionable insights into their latent beliefs and motivations. To address this, we evaluate Theory of Mind (ToM) approaches for Autonomous Cyber Operations. Upon learning a robust prior, ToM models can predict an agent's goals, behaviours, and contextual beliefs given only a handful of past behaviour observations. In this paper, we introduce a novel Graph Neural Network (GNN)-based ToM architecture tailored for cyber-defence, Graph-In, Graph-Out (GIGO)-ToM, which can accurately predict both the targets and attack trajectories of adversarial cyber agents over arbitrary computer network topologies. To evaluate the latter, we propose a novel extension of the Wasserstein distance for measuring the similarity of graph-based probability distributions. Whereas the standard Wasserstein distance lacks a fixed reference scale, we introduce a graph-theoretic normalization factor that enables a standardized comparison between networks of different sizes. We furnish this metric, which we term the Network Transport Distance (NTD), with a weighting function that emphasizes predictions according to custom node features, allowing network operators to explore arbitrary strategic considerations. Benchmarked against a Graph-In, Dense-Out (GIDO)-ToM architecture in an abstract cyber-defence environment, our empirical evaluations show that GIGO-ToM can accurately predict the goals and behaviours of various unseen cyber-attacking agents across a range of network topologies, as well as learn embeddings that can effectively characterize their policies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge