Lymphoma segmentation from 3D PET-CT images using a deep evidential network
Paper and Code
Jan 31, 2022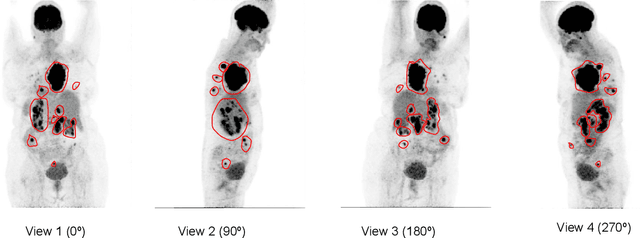
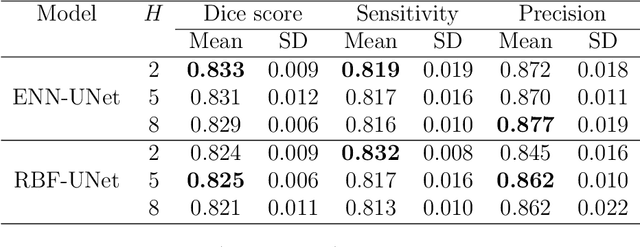
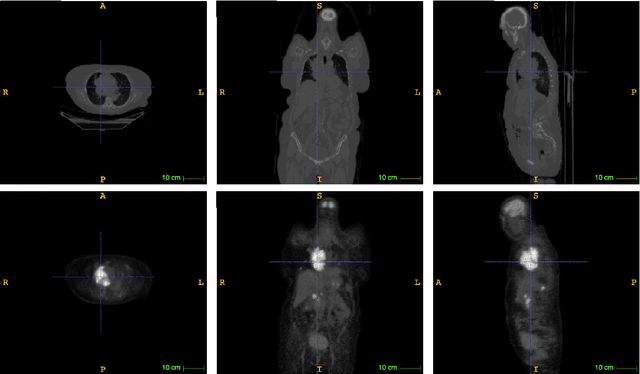
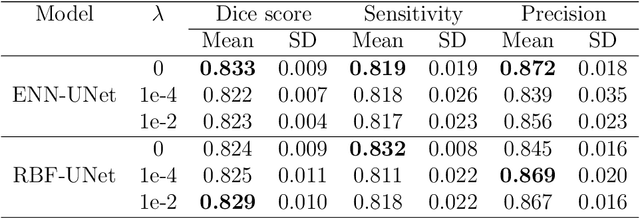
An automatic evidential segmentation method based on Dempster-Shafer theory and deep learning is proposed to segment lymphomas from three-dimensional Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Computed Tomography (CT) images. The architecture is composed of a deep feature-extraction module and an evidential layer. The feature extraction module uses an encoder-decoder framework to extract semantic feature vectors from 3D inputs. The evidential layer then uses prototypes in the feature space to compute a belief function at each voxel quantifying the uncertainty about the presence or absence of a lymphoma at this location. Two evidential layers are compared, based on different ways of using distances to prototypes for computing mass functions. The whole model is trained end-to-end by minimizing the Dice loss function. The proposed combination of deep feature extraction and evidential segmentation is shown to outperform the baseline UNet model as well as three other state-of-the-art models on a dataset of 173 patients.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge