LTSim: Layout Transportation-based Similarity Measure for Evaluating Layout Generation
Paper and Code
Jul 17, 2024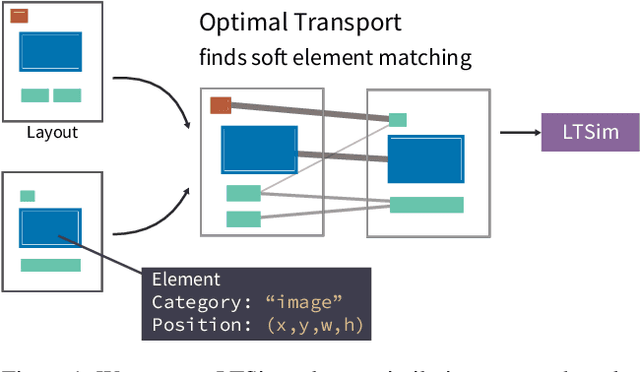
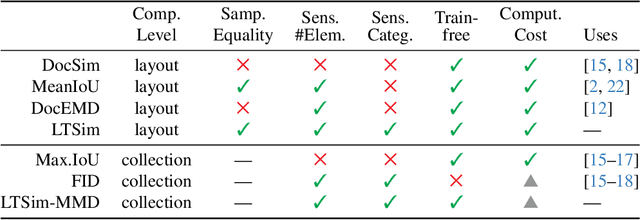
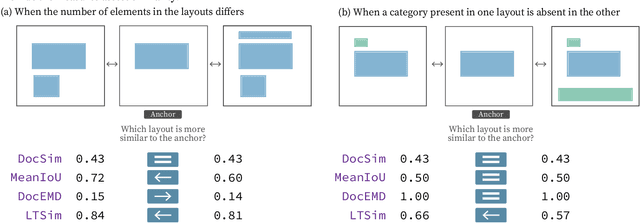
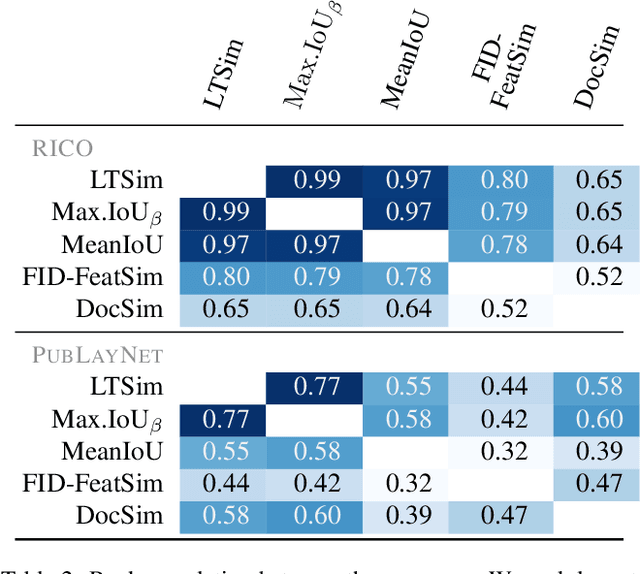
We introduce a layout similarity measure designed to evaluate the results of layout generation. While several similarity measures have been proposed in prior research, there has been a lack of comprehensive discussion about their behaviors. Our research uncovers that the majority of these measures are unable to handle various layout differences, primarily due to their dependencies on strict element matching, that is one-by-one matching of elements within the same category. To overcome this limitation, we propose a new similarity measure based on optimal transport, which facilitates a more flexible matching of elements. This approach allows us to quantify the similarity between any two layouts even those sharing no element categories, making our measure highly applicable to a wide range of layout generation tasks. For tasks such as unconditional layout generation, where FID is commonly used, we also extend our measure to deal with collection-level similarities between groups of layouts. The empirical result suggests that our collection-level measure offers more reliable comparisons than existing ones like FID and Max.IoU.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge