Low-dimensional Denoising Embedding Transformer for ECG Classification
Paper and Code
Mar 31, 2021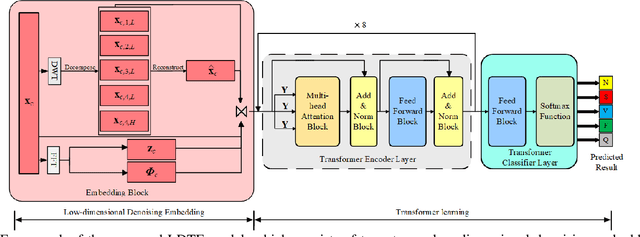
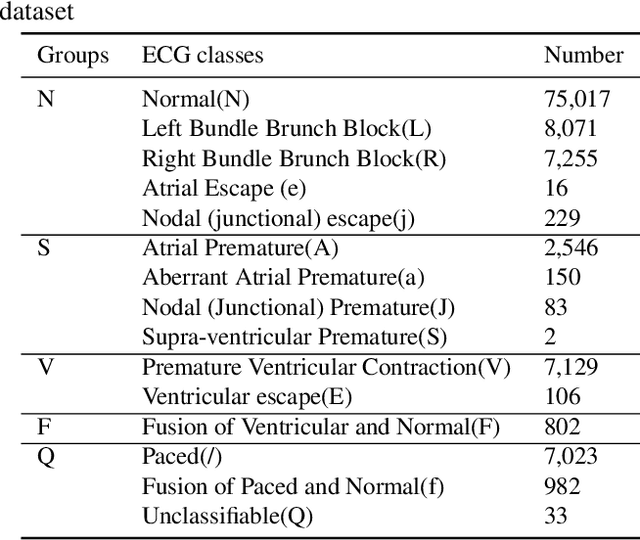

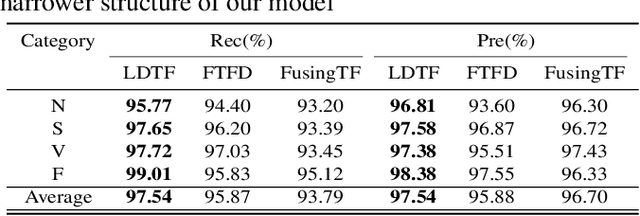
The transformer based model (e.g., FusingTF) has been employed recently for Electrocardiogram (ECG) signal classification. However, the high-dimensional embedding obtained via 1-D convolution and positional encoding can lead to the loss of the signal's own temporal information and a large amount of training parameters. In this paper, we propose a new method for ECG classification, called low-dimensional denoising embedding transformer (LDTF), which contains two components, i.e., low-dimensional denoising embedding (LDE) and transformer learning. In the LDE component, a low-dimensional representation of the signal is obtained in the time-frequency domain while preserving its own temporal information. And with the low dimensional embedding, the transformer learning is then used to obtain a deeper and narrower structure with fewer training parameters than that of the FusingTF. Experiments conducted on the MIT-BIH dataset demonstrates the effectiveness and the superior performance of our proposed method, as compared with state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge