Look-up and Adapt: A One-shot Semantic Parser
Paper and Code
Oct 27, 2019
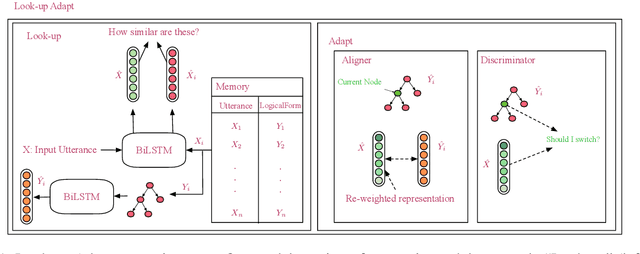


Computing devices have recently become capable of interacting with their end users via natural language. However, they can only operate within a limited "supported" domain of discourse and fail drastically when faced with an out-of-domain utterance, mainly due to the limitations of their semantic parser. In this paper, we propose a semantic parser that generalizes to out-of-domain examples by learning a general strategy for parsing an unseen utterance through adapting the logical forms of seen utterances, instead of learning to generate a logical form from scratch. Our parser maintains a memory consisting of a representative subset of the seen utterances paired with their logical forms. Given an unseen utterance, our parser works by looking up a similar utterance from the memory and adapting its logical form until it fits the unseen utterance. Moreover, we present a data generation strategy for constructing utterance-logical form pairs from different domains. Our results show an improvement of up to 68.8% on one-shot parsing under two different evaluation settings compared to the baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge