Limitations of Data-Driven Spectral Reconstruction -- An Optics-Aware Analysis
Paper and Code
Jan 08, 2024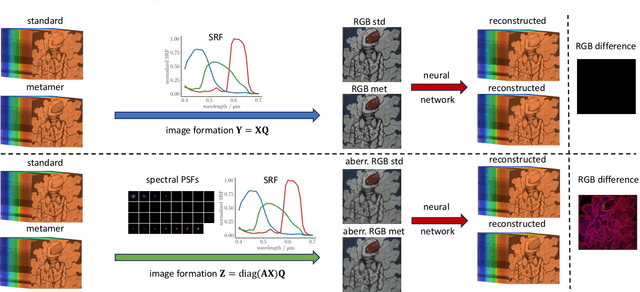
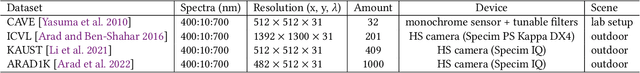
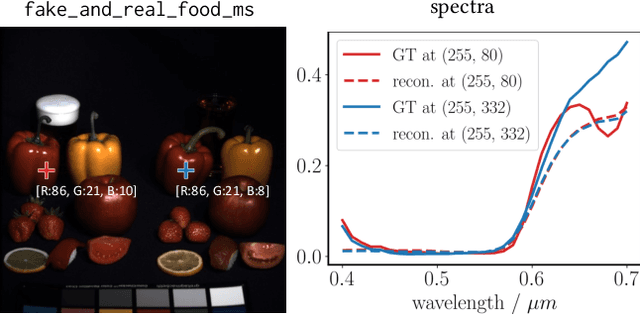
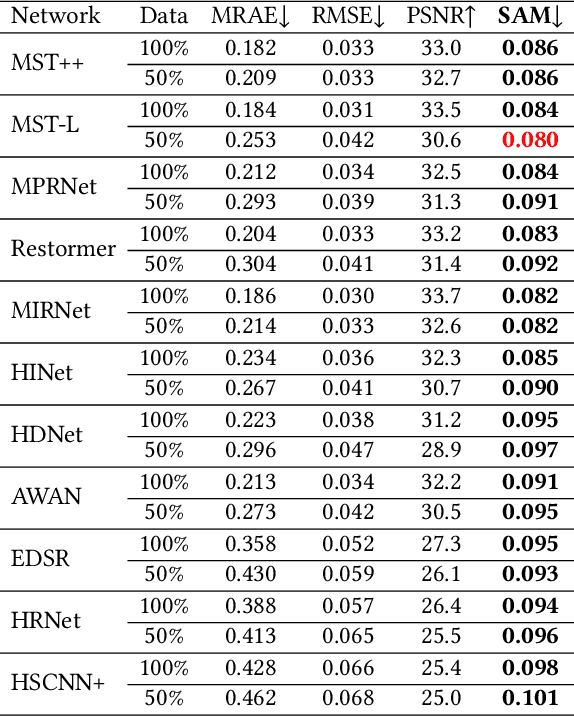
Hyperspectral imaging empowers computer vision systems with the distinct capability of identifying materials through recording their spectral signatures. Recent efforts in data-driven spectral reconstruction aim at extracting spectral information from RGB images captured by cost-effective RGB cameras, instead of dedicated hardware. In this paper we systematically analyze the performance of such methods, evaluating both the practical limitations with respect to current datasets and overfitting, as well as fundamental limits with respect to the nature of the information encoded in the RGB images, and the dependency of this information on the optical system of the camera. We find that the current models are not robust under slight variations, e.g., in noise level or compression of the RGB file. Both the methods and the datasets are also limited in their ability to cope with metameric colors. This issue can in part be overcome with metameric data augmentation. Moreover, optical lens aberrations can help to improve the encoding of the metameric information into the RGB image, which paves the road towards higher performing spectral imaging and reconstruction approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge