Leveraging Experience in Lazy Search
Paper and Code
Oct 10, 2021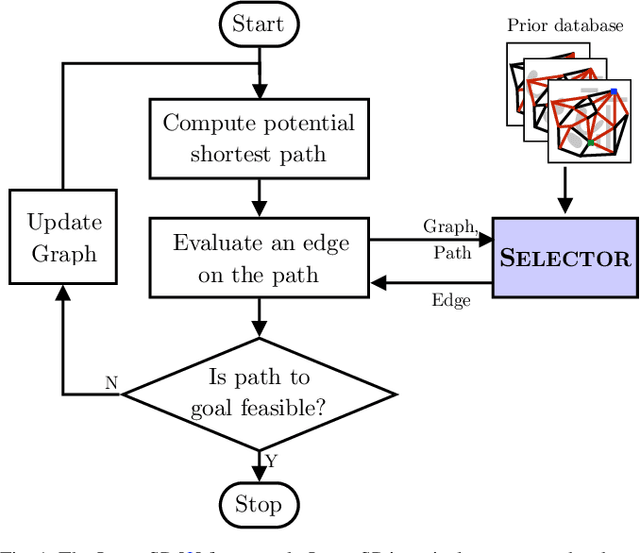
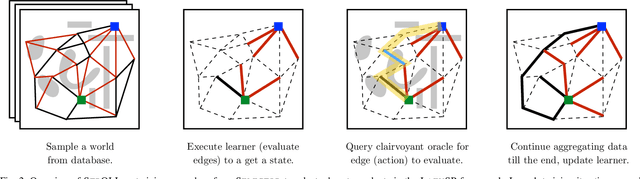
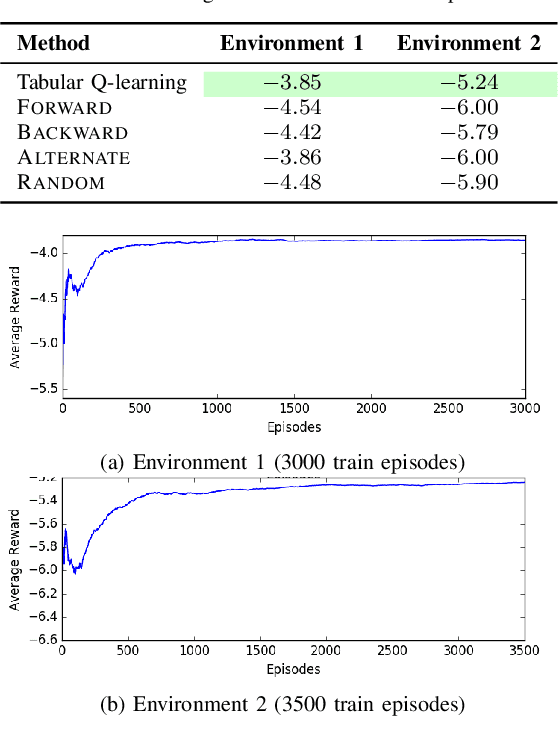
Lazy graph search algorithms are efficient at solving motion planning problems where edge evaluation is the computational bottleneck. These algorithms work by lazily computing the shortest potentially feasible path, evaluating edges along that path, and repeating until a feasible path is found. The order in which edges are selected is critical to minimizing the total number of edge evaluations: a good edge selector chooses edges that are not only likely to be invalid, but also eliminates future paths from consideration. We wish to learn such a selector by leveraging prior experience. We formulate this problem as a Markov Decision Process (MDP) on the state of the search problem. While solving this large MDP is generally intractable, we show that we can compute oracular selectors that can solve the MDP during training. With access to such oracles, we use imitation learning to find effective policies. If new search problems are sufficiently similar to problems solved during training, the learned policy will choose a good edge evaluation ordering and solve the motion planning problem quickly. We evaluate our algorithms on a wide range of 2D and 7D problems and show that the learned selector outperforms baseline commonly used heuristics. We further provide a novel theoretical analysis of lazy search in a Bayesian framework as well as regret guarantees on our imitation learning based approach to motion planning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge