Leveraging Allophony in Self-Supervised Speech Models for Atypical Pronunciation Assessment
Paper and Code
Feb 10, 2025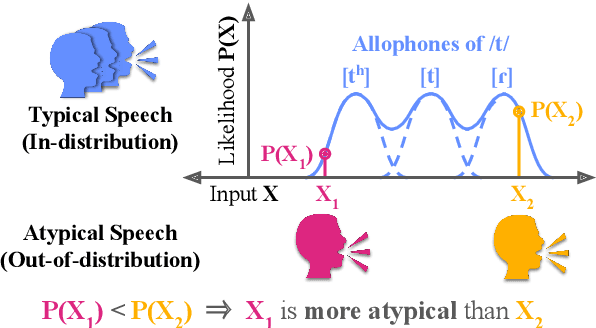
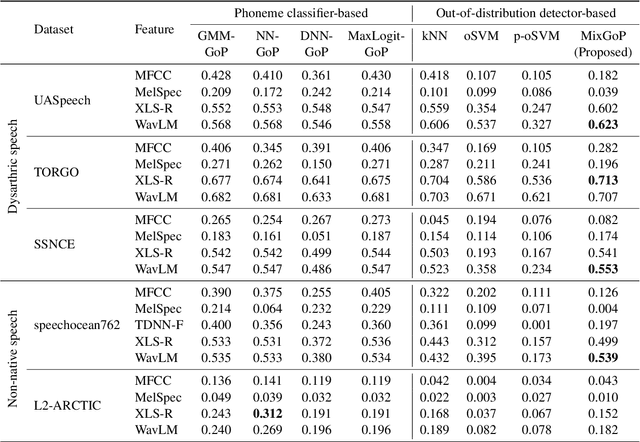
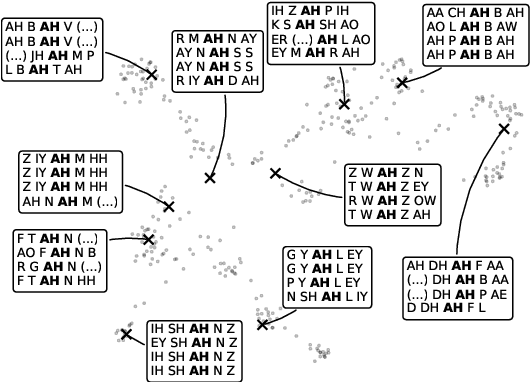
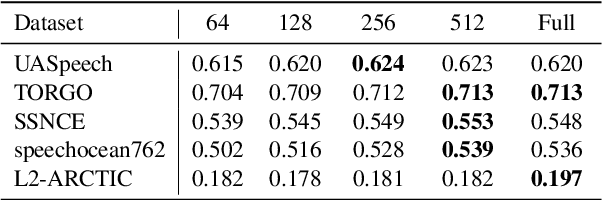
Allophony refers to the variation in the phonetic realization of a phoneme based on its phonetic environment. Modeling allophones is crucial for atypical pronunciation assessment, which involves distinguishing atypical from typical pronunciations. However, recent phoneme classifier-based approaches often simplify this by treating various realizations as a single phoneme, bypassing the complexity of modeling allophonic variation. Motivated by the acoustic modeling capabilities of frozen self-supervised speech model (S3M) features, we propose MixGoP, a novel approach that leverages Gaussian mixture models to model phoneme distributions with multiple subclusters. Our experiments show that MixGoP achieves state-of-the-art performance across four out of five datasets, including dysarthric and non-native speech. Our analysis further suggests that S3M features capture allophonic variation more effectively than MFCCs and Mel spectrograms, highlighting the benefits of integrating MixGoP with S3M features.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge