Learning with Instance Bundles for Reading Comprehension
Paper and Code
Apr 18, 2021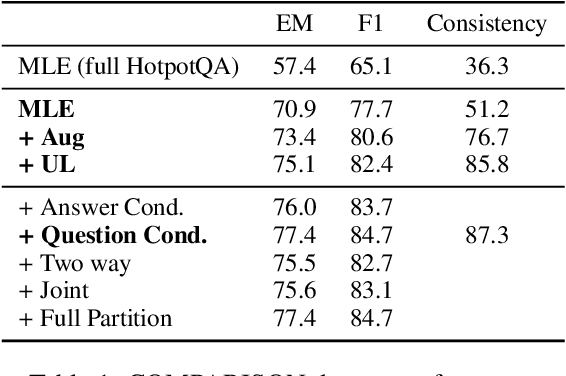
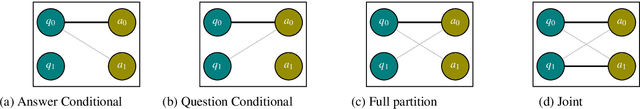
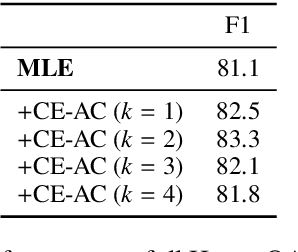
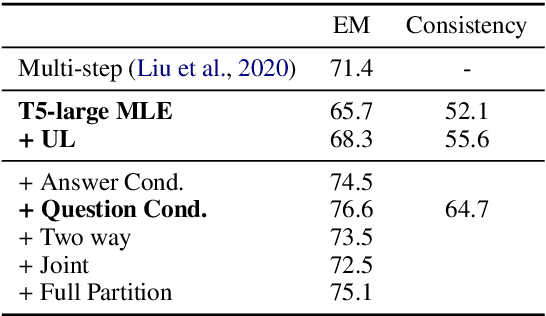
When training most modern reading comprehension models, all the questions associated with a context are treated as being independent from each other. However, closely related questions and their corresponding answers are not independent, and leveraging these relationships could provide a strong supervision signal to a model. Drawing on ideas from contrastive estimation, we introduce several new supervision techniques that compare question-answer scores across multiple related instances. Specifically, we normalize these scores across various neighborhoods of closely contrasting questions and/or answers, adding another cross entropy loss term that is used in addition to traditional maximum likelihood estimation. Our techniques require bundles of related question-answer pairs, which we can either mine from within existing data or create using various automated heuristics. We empirically demonstrate the effectiveness of training with instance bundles on two datasets -- HotpotQA and ROPES -- showing up to 11% absolute gains in accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge