Learning to Align Images using Weak Geometric Supervision
Paper and Code
Aug 04, 2018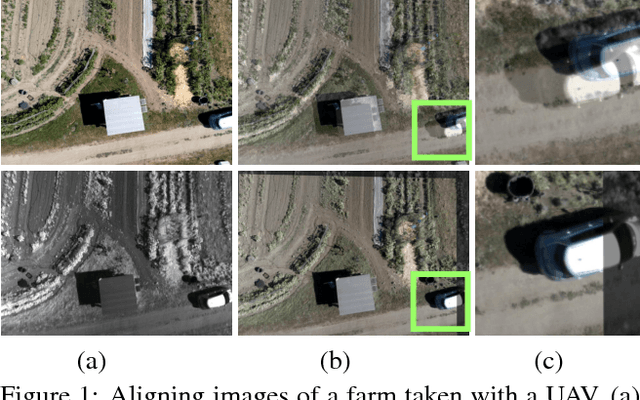
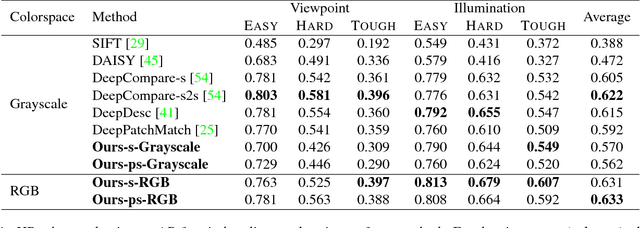
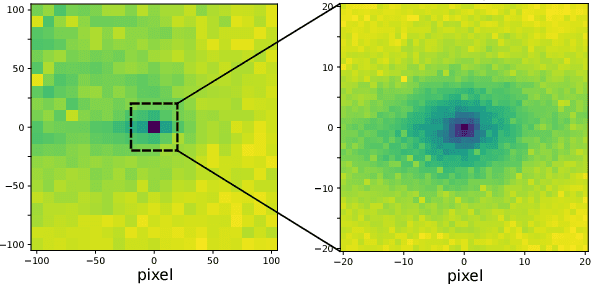
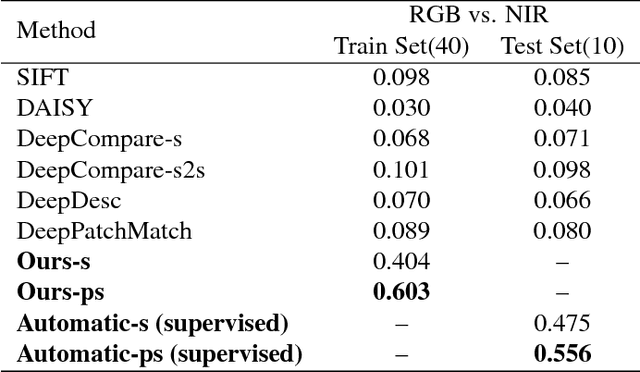
Image alignment tasks require accurate pixel correspondences, which are usually recovered by matching local feature descriptors. Such descriptors are often derived using supervised learning on existing datasets with ground truth correspondences. However, the cost of creating such datasets is usually prohibitive. In this paper, we propose a new approach to align two images related by an unknown 2D homography where the local descriptor is learned from scratch from the images and the homography is estimated simultaneously. Our key insight is that a siamese convolutional neural network can be trained jointly while iteratively updating the homography parameters by optimizing a single loss function. Our method is currently weakly supervised because the input images need to be roughly aligned. We have used this method to align images of different modalities such as RGB and near-infra-red (NIR) without using any prior labeled data. Images automatically aligned by our method were then used to train descriptors that generalize to new images. We also evaluated our method on RGB images. On the HPatches benchmark, our method achieves comparable accuracy to deep local descriptors that were trained offline in a supervised setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge