Learning Interpretable Queries for Explainable Image Classification with Information Pursuit
Paper and Code
Dec 16, 2023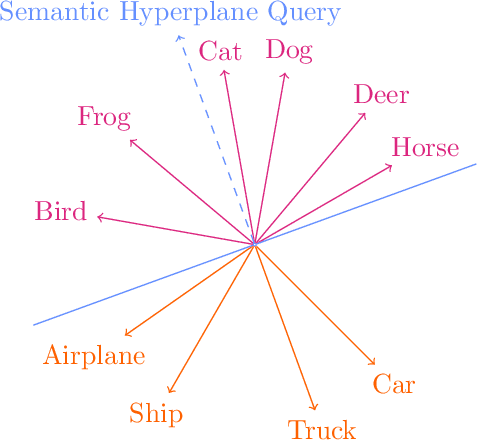
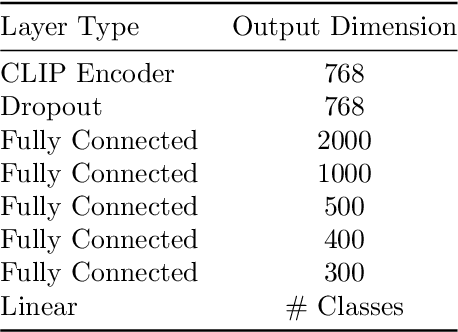
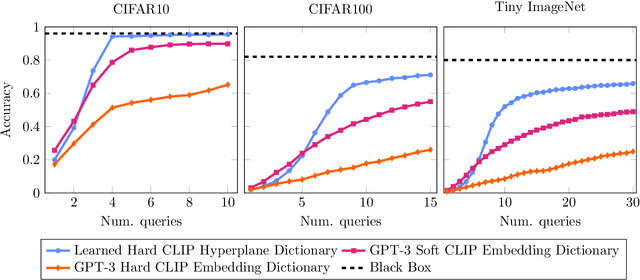
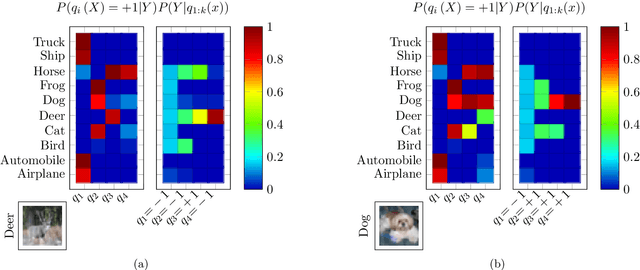
Information Pursuit (IP) is an explainable prediction algorithm that greedily selects a sequence of interpretable queries about the data in order of information gain, updating its posterior at each step based on observed query-answer pairs. The standard paradigm uses hand-crafted dictionaries of potential data queries curated by a domain expert or a large language model after a human prompt. However, in practice, hand-crafted dictionaries are limited by the expertise of the curator and the heuristics of prompt engineering. This paper introduces a novel approach: learning a dictionary of interpretable queries directly from the dataset. Our query dictionary learning problem is formulated as an optimization problem by augmenting IP's variational formulation with learnable dictionary parameters. To formulate learnable and interpretable queries, we leverage the latent space of large vision and language models like CLIP. To solve the optimization problem, we propose a new query dictionary learning algorithm inspired by classical sparse dictionary learning. Our experiments demonstrate that learned dictionaries significantly outperform hand-crafted dictionaries generated with large language models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge