Large-Field Contextual Feature Learning for Glass Detection
Paper and Code
Sep 10, 2022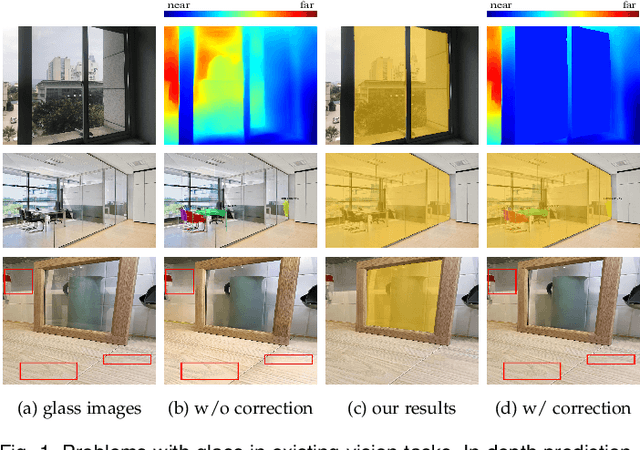
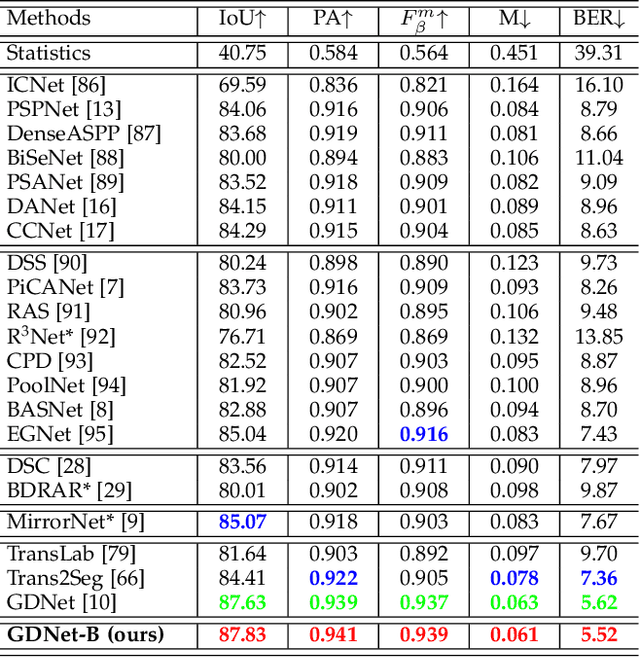

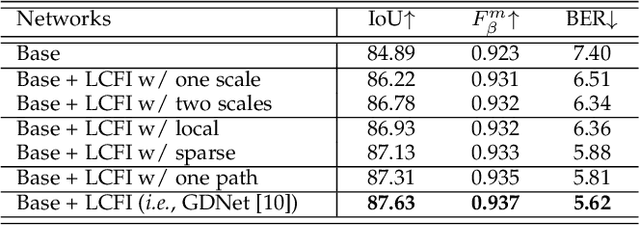
Glass is very common in our daily life. Existing computer vision systems neglect it and thus may have severe consequences, e.g., a robot may crash into a glass wall. However, sensing the presence of glass is not straightforward. The key challenge is that arbitrary objects/scenes can appear behind the glass. In this paper, we propose an important problem of detecting glass surfaces from a single RGB image. To address this problem, we construct the first large-scale glass detection dataset (GDD) and propose a novel glass detection network, called GDNet-B, which explores abundant contextual cues in a large field-of-view via a novel large-field contextual feature integration (LCFI) module and integrates both high-level and low-level boundary features with a boundary feature enhancement (BFE) module. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our GDNet-B achieves satisfying glass detection results on the images within and beyond the GDD testing set. We further validate the effectiveness and generalization capability of our proposed GDNet-B by applying it to other vision tasks, including mirror segmentation and salient object detection. Finally, we show the potential applications of glass detection and discuss possible future research directions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge