Language Models that Seek for Knowledge: Modular Search & Generation for Dialogue and Prompt Completion
Paper and Code
Mar 29, 2022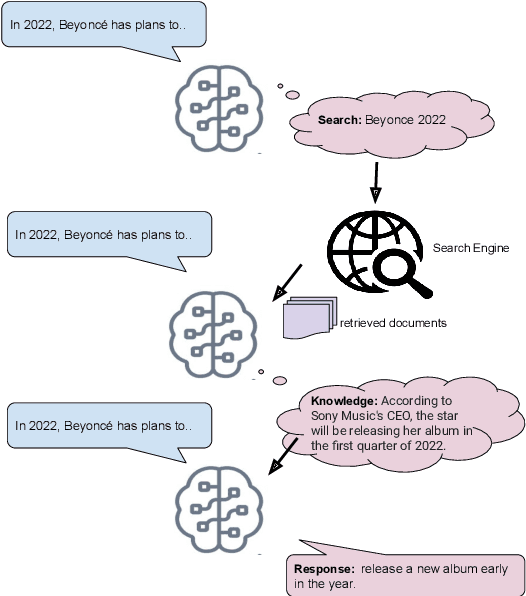

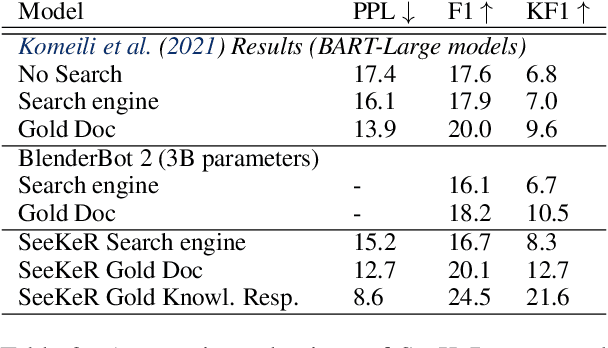

Language models (LMs) have recently been shown to generate more factual responses by employing modularity (Zhou et al., 2021) in combination with retrieval (Adolphs et al., 2021). We extend the recent approach of Adolphs et al. (2021) to include internet search as a module. Our SeeKeR (Search engine->Knowledge->Response) method thus applies a single LM to three modular tasks in succession: search, generating knowledge, and generating a final response. We show that, when using SeeKeR as a dialogue model, it outperforms the state-of-the-art model BlenderBot 2 (Chen et al., 2021) on open-domain knowledge-grounded conversations for the same number of parameters, in terms of consistency, knowledge and per-turn engagingness. SeeKeR applied to topical prompt completions as a standard language model outperforms GPT2 (Radford et al., 2019) and GPT3 (Brown et al., 2020) in terms of factuality and topicality, despite GPT3 being a vastly larger model. Our code and models are made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge