L2GSCI: Local to Global Seam Cutting and Integrating for Accurate Face Contour Extraction
Paper and Code
Mar 05, 2017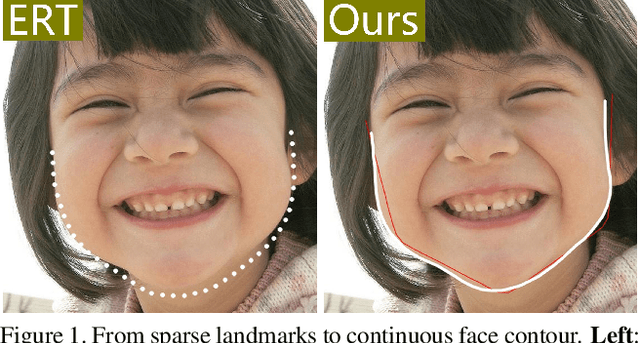
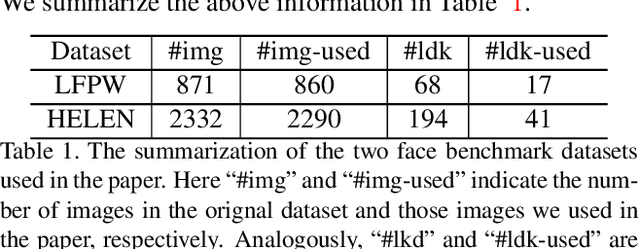
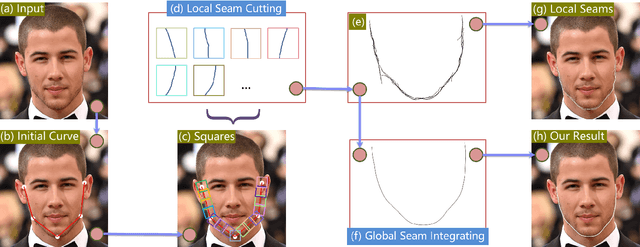
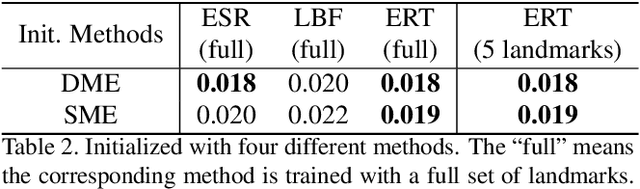
Current face alignment algorithms can robustly find a set of landmarks along face contour. However, the landmarks are sparse and lack curve details, especially in chin and cheek areas where a lot of concave-convex bending information exists. In this paper, we propose a local to global seam cutting and integrating algorithm (L2GSCI) to extract continuous and accurate face contour. Our method works in three steps with the help of a rough initial curve. First, we sample small and overlapped squares along the initial curve. Second, the seam cutting part of L2GSCI extracts a local seam in each square region. Finally, the seam integrating part of L2GSCI connects all the redundant seams together to form a continuous and complete face curve. Overall, the proposed method is much more straightforward than existing face alignment algorithms, but can achieve pixel-level continuous face curves rather than discrete and sparse landmarks. Moreover, experiments on two face benchmark datasets (i.e., LFPW and HELEN) show that our method can precisely reveal concave-convex bending details of face contours, which has significantly improved the performance when compared with the state-ofthe- art face alignment approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge