Joint Identifiability of Cross-Domain Recommendation via Hierarchical Subspace Disentanglement
Paper and Code
Apr 06, 2024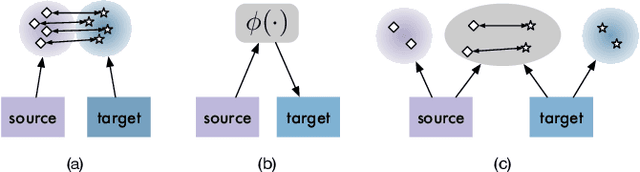
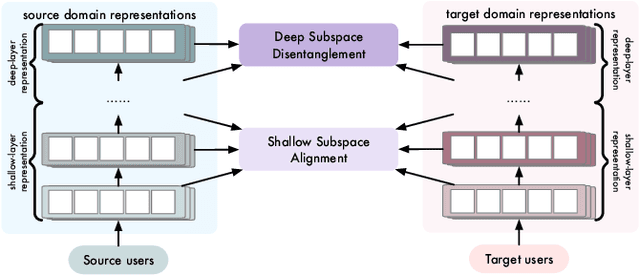
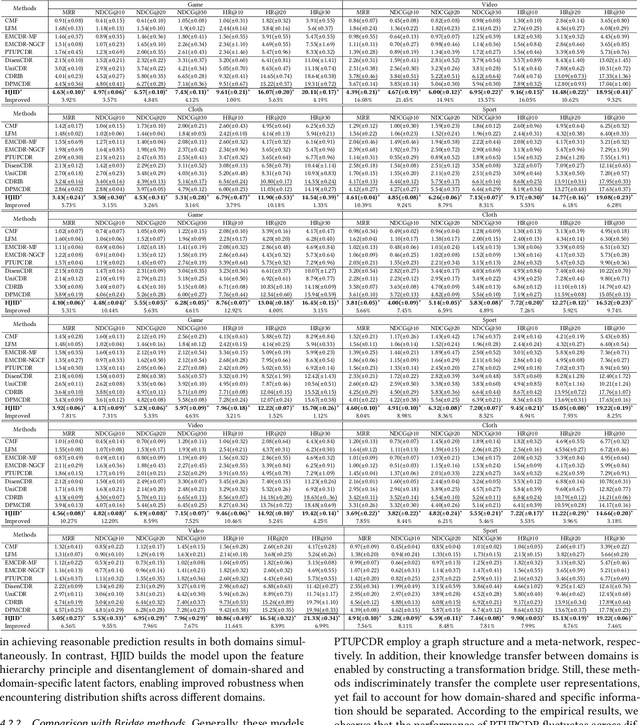
Cross-Domain Recommendation (CDR) seeks to enable effective knowledge transfer across domains. Existing works rely on either representation alignment or transformation bridges, but they struggle on identifying domain-shared from domain-specific latent factors. Specifically, while CDR describes user representations as a joint distribution over two domains, these methods fail to account for its joint identifiability as they primarily fixate on the marginal distribution within a particular domain. Such a failure may overlook the conditionality between two domains and how it contributes to latent factor disentanglement, leading to negative transfer when domains are weakly correlated. In this study, we explore what should and should not be transferred in cross-domain user representations from a causality perspective. We propose a Hierarchical subspace disentanglement approach to explore the Joint IDentifiability of cross-domain joint distribution, termed HJID, to preserve domain-specific behaviors from domain-shared factors. HJID organizes user representations into layers: generic shallow subspaces and domain-oriented deep subspaces. We first encode the generic pattern in the shallow subspace by minimizing the Maximum Mean Discrepancy of initial layer activation. Then, to dissect how domain-oriented latent factors are encoded in deeper layers activation, we construct a cross-domain causality-based data generation graph, which identifies cross-domain consistent and domain-specific components, adhering to the Minimal Change principle. This allows HJID to maintain stability whilst discovering unique factors for different domains, all within a generative framework of invertible transformations that guarantee the joint identifiability. With experiments on real-world datasets, we show that HJID outperforms SOTA methods on a range of strongly and weakly correlated CDR tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge