It Is Not the Journey but the Destination: Endpoint Conditioned Trajectory Prediction
Paper and Code
Apr 04, 2020
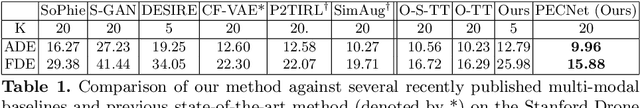
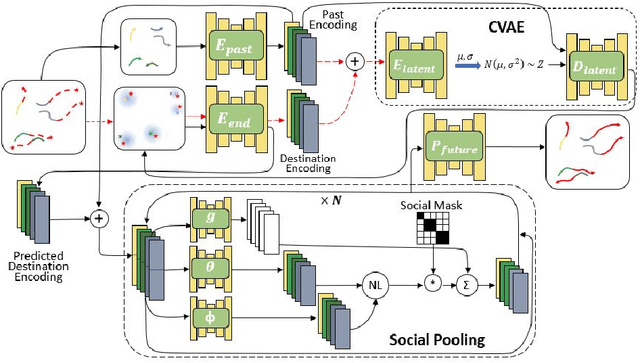
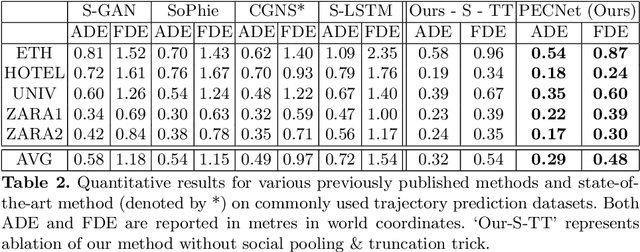
Human trajectory forecasting with multiple socially interacting agents is of critical importance for autonomous navigation in human environments, e.g., for self-driving cars and social robots. In this work, we present Predicted Endpoint Conditioned Network (PECNet) for flexible human trajectory prediction. PECNet infers distant trajectory endpoints to assist in long-range multi-modal trajectory prediction. A novel non-local social pooling layer enables PECNet to infer diverse yet socially compliant trajectories. Additionally, we present a simple "truncation-trick" for improving few-shot multi-modal trajectory prediction performance. We show that PECNet improves state-of-the-art performance on the Stanford Drone trajectory prediction benchmark by ~19.5% and on the ETH/UCY benchmark by ~40.8%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge