Intra-Retinal Layer Segmentation of 3D Optical Coherence Tomography Using Coarse Grained Diffusion Map
Paper and Code
Oct 08, 2012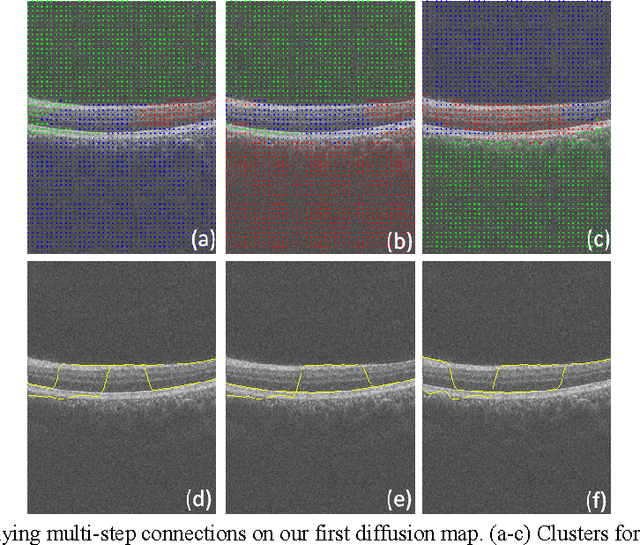
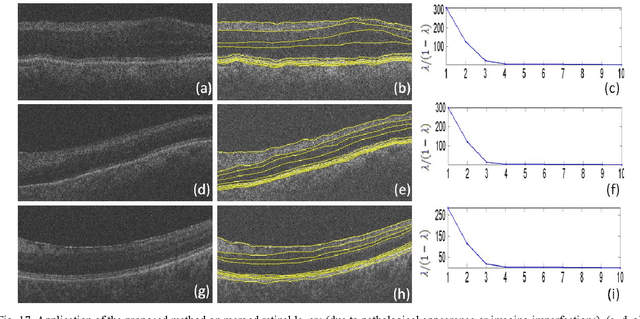
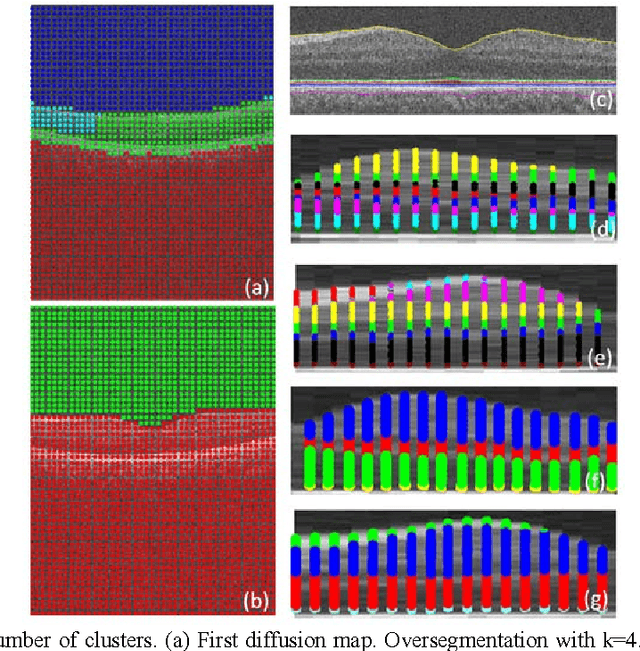

Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a powerful and noninvasive method for retinal imaging. In this paper, we introduce a fast segmentation method based on a new variant of spectral graph theory named diffusion maps. The research is performed on spectral domain (SD) OCT images depicting macular and optic nerve head appearance. The presented approach does not require edge-based image information and relies on regional image texture. Consequently, the proposed method demonstrates robustness in situations of low image contrast or poor layer-to-layer image gradients. Diffusion mapping is applied to 2D and 3D OCT datasets composed of two steps, one for partitioning the data into important and less important sections, and another one for localization of internal layers.In the first step, the pixels/voxels are grouped in rectangular/cubic sets to form a graph node.The weights of a graph are calculated based on geometric distances between pixels/voxels and differences of their mean intensity.The first diffusion map clusters the data into three parts, the second of which is the area of interest. The other two sections are eliminated from the remaining calculations. In the second step, the remaining area is subjected to another diffusion map assessment and the internal layers are localized based on their textural similarities.The proposed method was tested on 23 datasets from two patient groups (glaucoma and normals). The mean unsigned border positioning errors(mean - SD) was 8.52 - 3.13 and 7.56 - 2.95 micrometer for the 2D and 3D methods, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge