Interpretable Deep Learning for Pattern Recognition in Brain Differences Between Men and Women
Paper and Code
Jun 20, 2020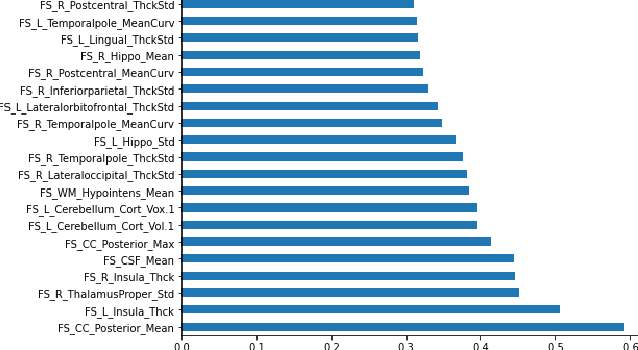
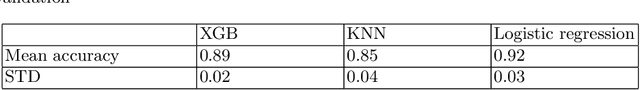
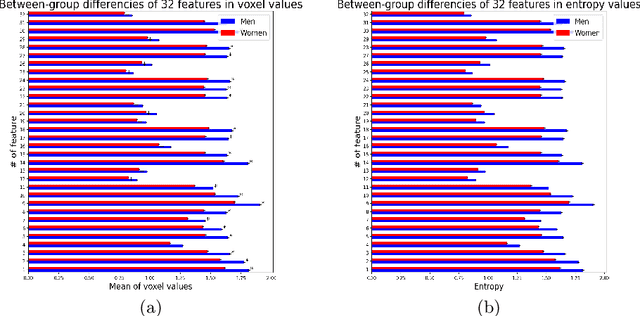
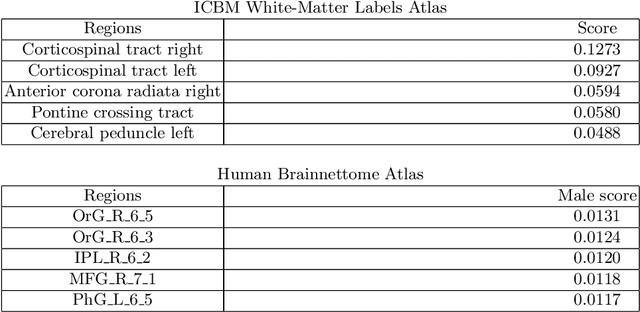
Deep learning shows high potential for many medical image analysis tasks. Neural networks work with full-size data without extensive preprocessing and feature generation and, thus, information loss. Recent work has shown that morphological difference between specific brain regions can be found on MRI with deep learning techniques. We consider the pattern recognition task based on a large open-access dataset of healthy subjects - an exploration of brain differences between men and women. However, interpretation of the lately proposed models is based on a region of interest and can not be extended to pixel or voxel-wise image interpretation, which is considered to be more informative. In this paper, we confirm the previous findings in sex differences from diffusion-tensor imaging on T1 weighted brain MRI scans. We compare the results of three voxel-based 3D CNN interpretation methods: Meaningful Perturbations, GradCam and Guided Backpropagation and provide the open-source code.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge