Instance- and Category-level 6D Object Pose Estimation
Paper and Code
Mar 11, 2019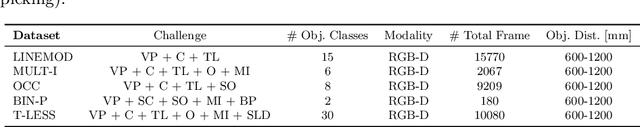
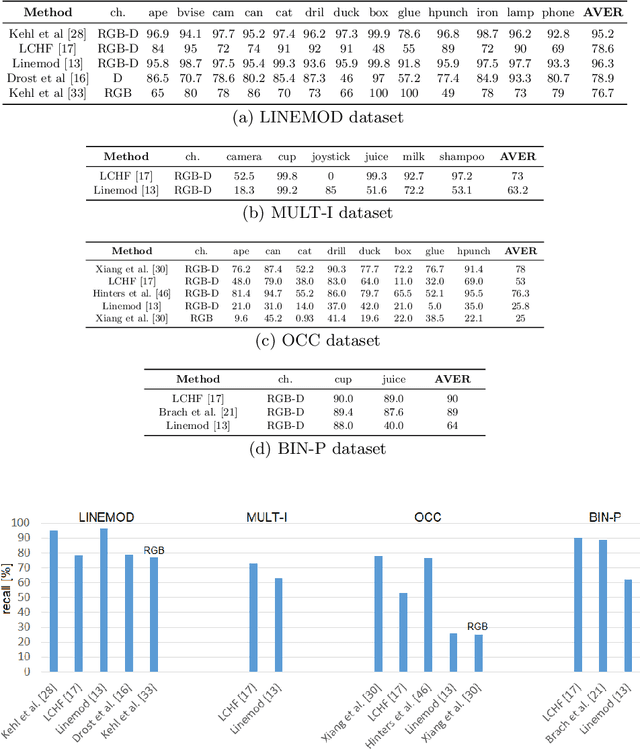
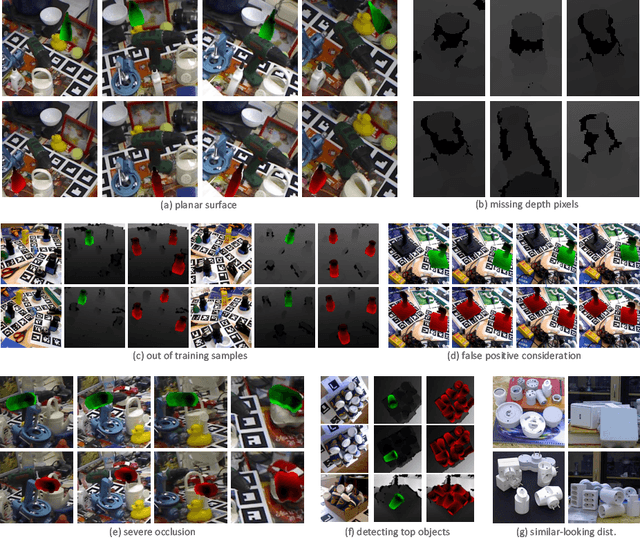
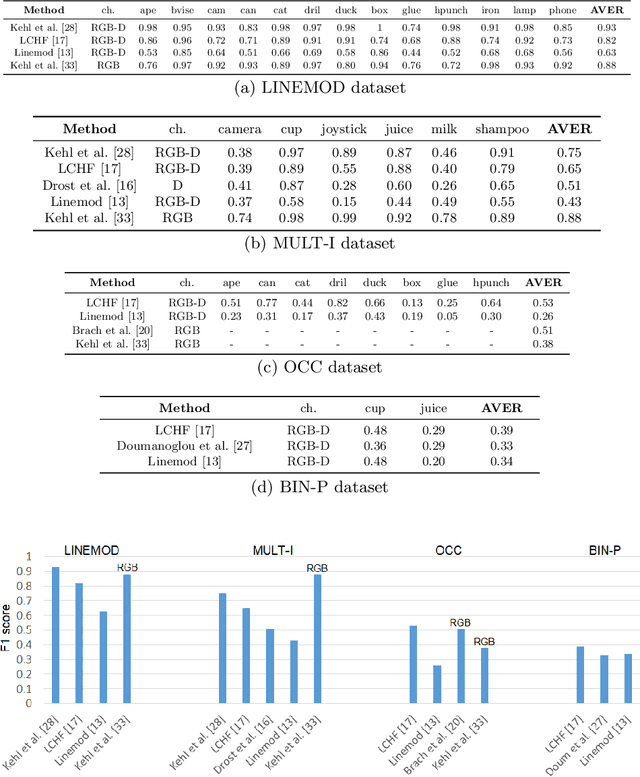
6D object pose estimation is an important task that determines the 3D position and 3D rotation of an object in camera-centred coordinates. By utilizing such a task, one can propose promising solutions for various problems related to scene understanding, augmented reality, control and navigation of robotics. Recent developments on visual depth sensors and low-cost availability of depth data significantly facilitate object pose estimation. Using depth information from RGB-D sensors, substantial progress has been made in the last decade by the methods addressing the challenges such as viewpoint variability, occlusion and clutter, and similar looking distractors. Particularly, with the recent advent of convolutional neural networks, RGB-only based solutions have been presented. However, improved results have only been reported for recovering the pose of known instances, i.e., for the instance-level object pose estimation tasks. More recently, state-of-the-art approaches target to solve object pose estimation problem at the level of categories, recovering the 6D pose of unknown instances. To this end, they address the challenges of the category-level tasks such as distribution shift among source and target domains, high intra-class variations, and shape discrepancies between objects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge