Input Length Matters: An Empirical Study Of RNN-T And MWER Training For Long-form Telephony Speech Recognition
Paper and Code
Oct 08, 2021
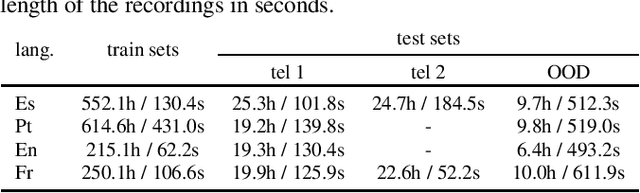
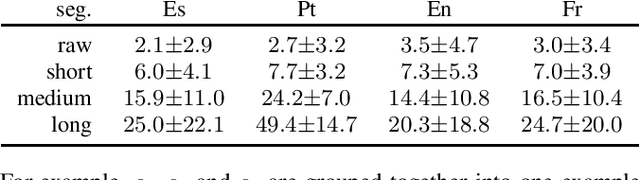

End-to-end models have achieved state-of-the-art results on several automatic speech recognition tasks. However, they perform poorly when evaluated on long-form data, e.g., minutes long conversational telephony audio. One reason the model fails on long-form speech is that it has only seen short utterances during training. This paper presents an empirical study on the effect of training utterance length on the word error rate (WER) for RNN-transducer (RNN-T) model. We compare two widely used training objectives, log loss (or RNN-T loss) and minimum word error rate (MWER) loss. We conduct experiments on telephony datasets in four languages. Our experiments show that for both losses, the WER on long-form speech reduces substantially as the training utterance length increases. The average relative WER gain is 15.7% for log loss and 8.8% for MWER loss. When training on short utterances, MWER loss leads to a lower WER than the log loss. Such difference between the two losses diminishes when the input length increases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge