Inharmonious Region Localization via Recurrent Self-Reasoning
Paper and Code
Oct 05, 2022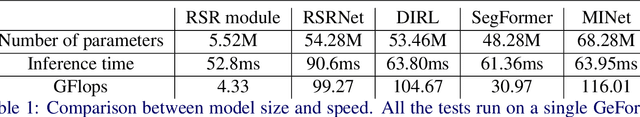

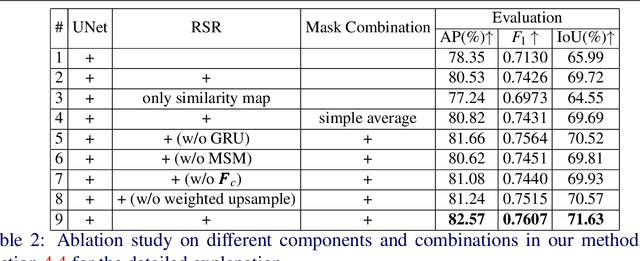
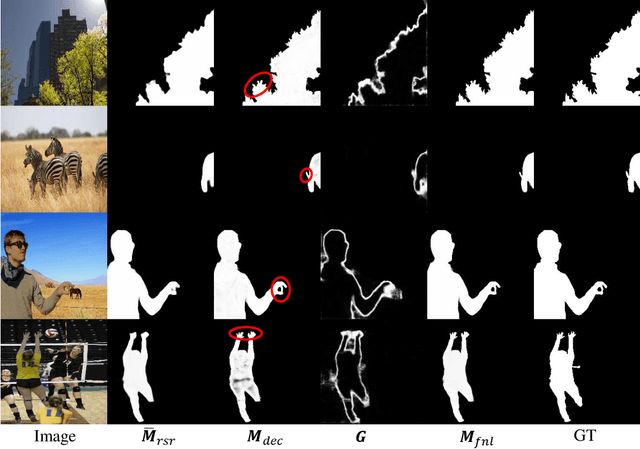
Synthetic images created by image editing operations are prevalent, but the color or illumination inconsistency between the manipulated region and background may make it unrealistic. Thus, it is important yet challenging to localize the inharmonious region to improve the quality of synthetic image. Inspired by the classic clustering algorithm, we aim to group pixels into two clusters: inharmonious cluster and background cluster by inserting a novel Recurrent Self-Reasoning (RSR) module into the bottleneck of UNet structure. The mask output from RSR module is provided for the decoder as attention guidance. Finally, we adaptively combine the masks from RSR and the decoder to form our final mask. Experimental results on the image harmonization dataset demonstrate that our method achieves competitive performance both quantitatively and qualitatively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge