Information-theoretic Abstraction of Semantic Octree Models for Integrated Perception and Planning
Paper and Code
Sep 20, 2022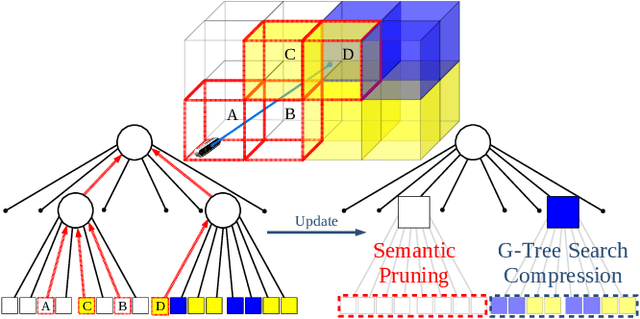

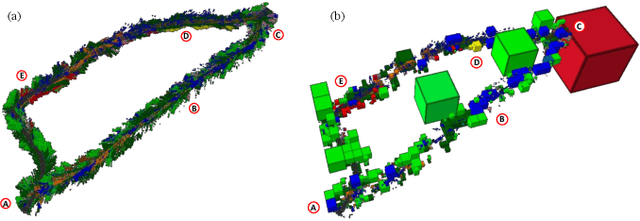
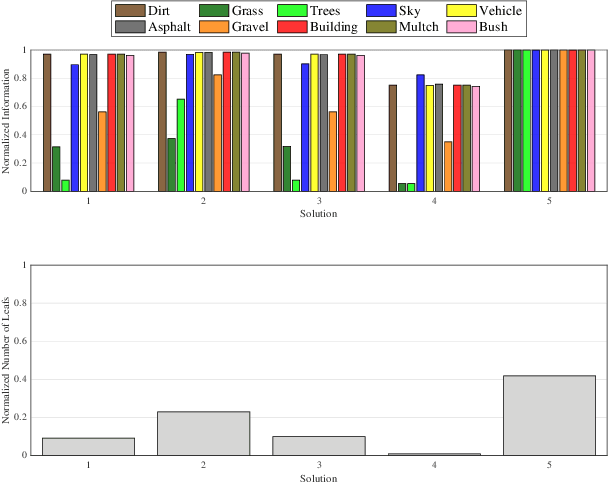
In this paper, we develop an approach that enables autonomous robots to build and compress semantic environment representations from point-cloud data. Our approach builds a three-dimensional, semantic tree representation of the environment from sensor data which is then compressed by a novel information-theoretic tree-pruning approach. The proposed approach is probabilistic and incorporates the uncertainty in semantic classification inherent in real-world environments. Moreover, our approach allows robots to prioritize individual semantic classes when generating the compressed trees, so as to design multi-resolution representations that retain the relevant semantic information while simultaneously discarding unwanted semantic categories. We demonstrate the approach by compressing semantic octree models of a large outdoor, semantically rich, real-world environment. In addition, we show how the octree abstractions can be used to create semantically-informed graphs for motion planning, and provide a comparison of our approach with uninformed graph construction methods such as Halton sequences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge