Incorporating Task-Specific Structural Knowledge into CNNs for Brain Midline Shift Detection
Paper and Code
Aug 13, 2019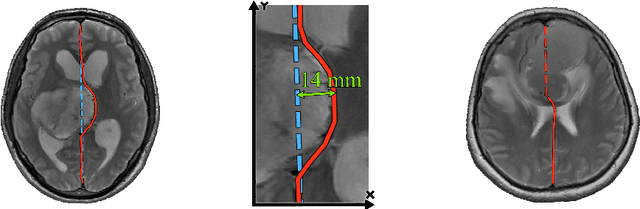
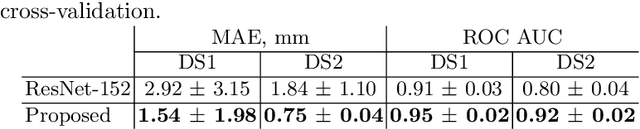
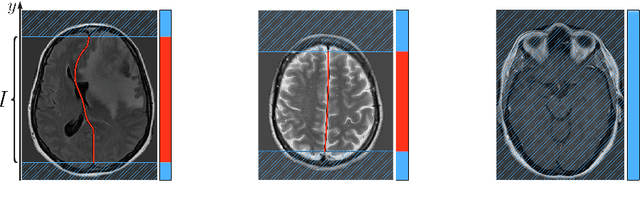
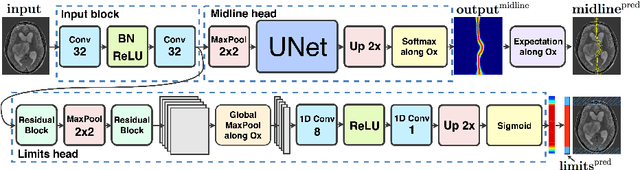
Midline shift (MLS) is a well-established factor used for outcome prediction in traumatic brain injury, stroke and brain tumors. The importance of automatic estimation of MLS was recently highlighted by ACR Data Science Institute. In this paper we introduce a novel deep learning based approach for the problem of MLS detection, which exploits task-specific structural knowledge. We evaluate our method on a large dataset containing heterogeneous images with significant MLS and show that its mean error approaches the inter-expert variability. Finally, we show the robustness of our approach by validating it on an external dataset, acquired during routine clinical practice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge