Improving Molecular Modeling with Geometric GNNs: an Empirical Study
Paper and Code
Jul 11, 2024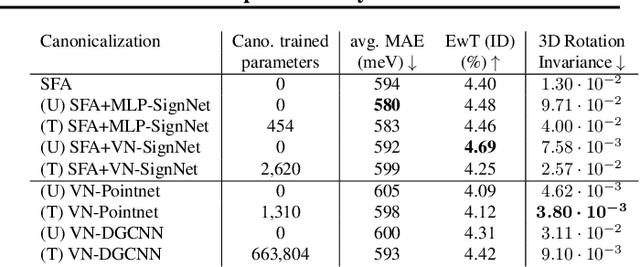

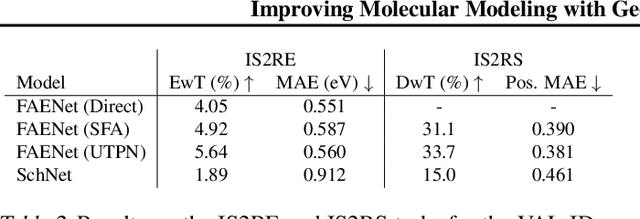

Rapid advancements in machine learning (ML) are transforming materials science by significantly speeding up material property calculations. However, the proliferation of ML approaches has made it challenging for scientists to keep up with the most promising techniques. This paper presents an empirical study on Geometric Graph Neural Networks for 3D atomic systems, focusing on the impact of different (1) canonicalization methods, (2) graph creation strategies, and (3) auxiliary tasks, on performance, scalability and symmetry enforcement. Our findings and insights aim to guide researchers in selecting optimal modeling components for molecular modeling tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge