Improving Compositional Generalization with Latent Structure and Data Augmentation
Paper and Code
Dec 14, 2021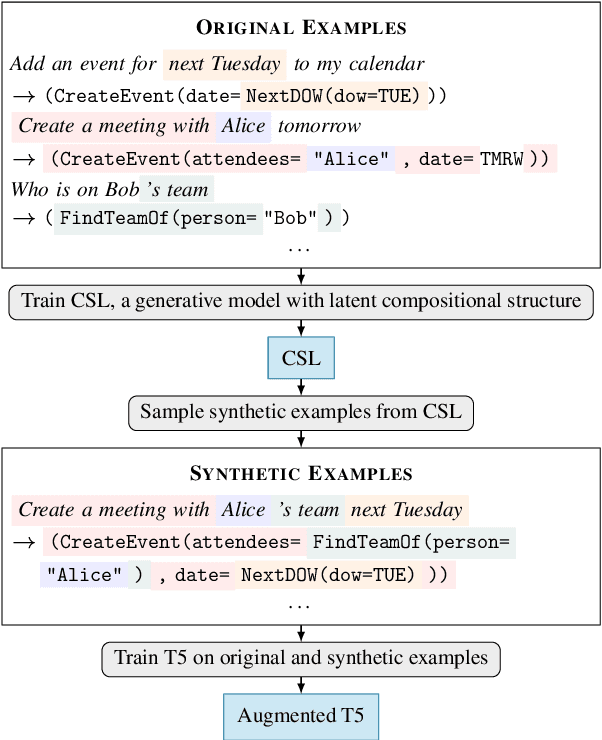
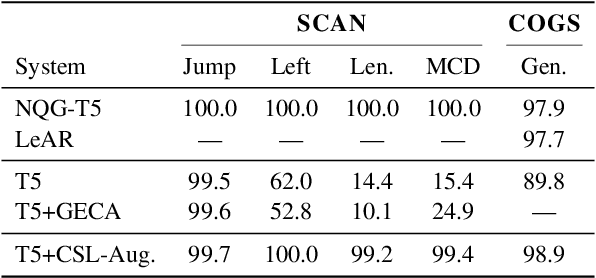
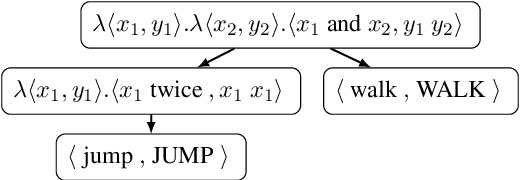
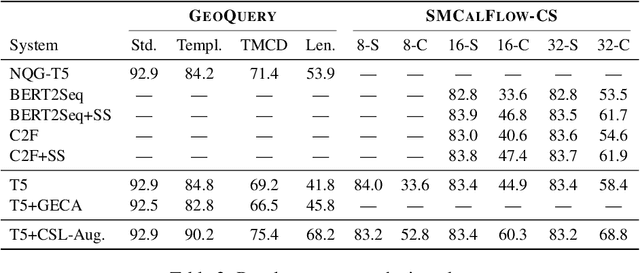
Generic unstructured neural networks have been shown to struggle on out-of-distribution compositional generalization. Compositional data augmentation via example recombination has transferred some prior knowledge about compositionality to such black-box neural models for several semantic parsing tasks, but this often required task-specific engineering or provided limited gains. We present a more powerful data recombination method using a model called Compositional Structure Learner (CSL). CSL is a generative model with a quasi-synchronous context-free grammar backbone, which we induce from the training data. We sample recombined examples from CSL and add them to the fine-tuning data of a pre-trained sequence-to-sequence model (T5). This procedure effectively transfers most of CSL's compositional bias to T5 for diagnostic tasks, and results in a model even stronger than a T5-CSL ensemble on two real world compositional generalization tasks. This results in new state-of-the-art performance for these challenging semantic parsing tasks requiring generalization to both natural language variation and novel compositions of elements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge