Improved and Efficient Text Adversarial Attacks using Target Information
Paper and Code
May 02, 2021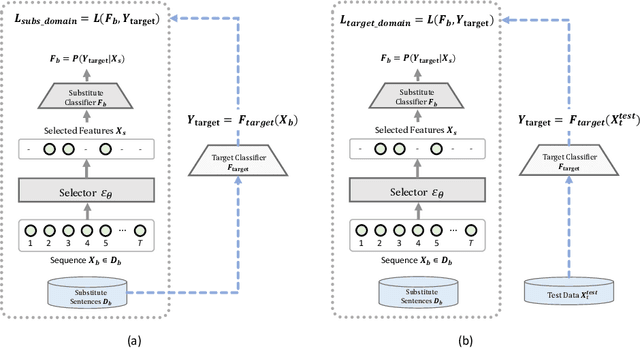
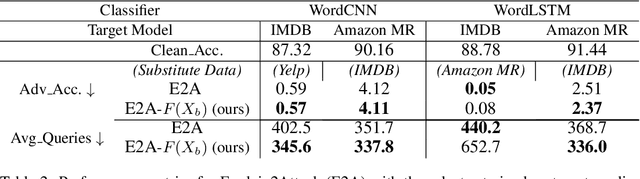
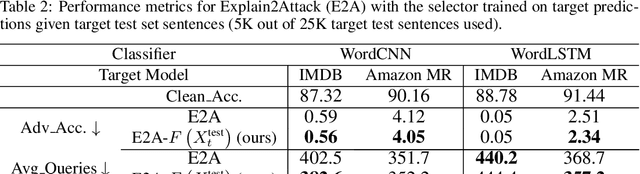
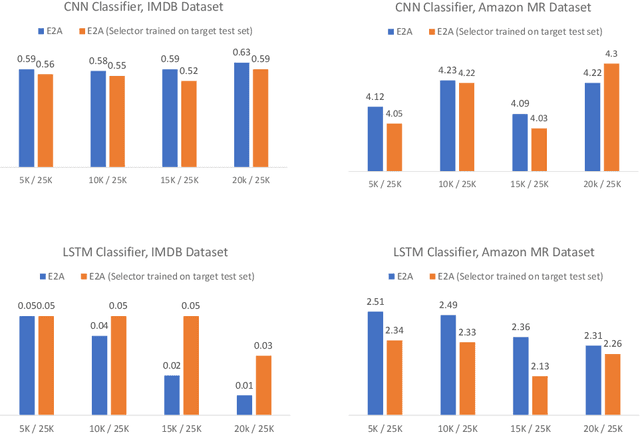
There has been recently a growing interest in studying adversarial examples on natural language models in the black-box setting. These methods attack natural language classifiers by perturbing certain important words until the classifier label is changed. In order to find these important words, these methods rank all words by importance by querying the target model word by word for each input sentence, resulting in high query inefficiency. A new interesting approach was introduced that addresses this problem through interpretable learning to learn the word ranking instead of previous expensive search. The main advantage of using this approach is that it achieves comparable attack rates to the state-of-the-art methods, yet faster and with fewer queries, where fewer queries are desirable to avoid suspicion towards the attacking agent. Nonetheless, this approach sacrificed the useful information that could be leveraged from the target classifier for that sake of query efficiency. In this paper we study the effect of leveraging the target model outputs and data on both attack rates and average number of queries, and we show that both can be improved, with a limited overhead of additional queries.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge