Improve Global Glomerulosclerosis Classification with Imbalanced Data using CircleMix Augmentation
Paper and Code
Jan 16, 2021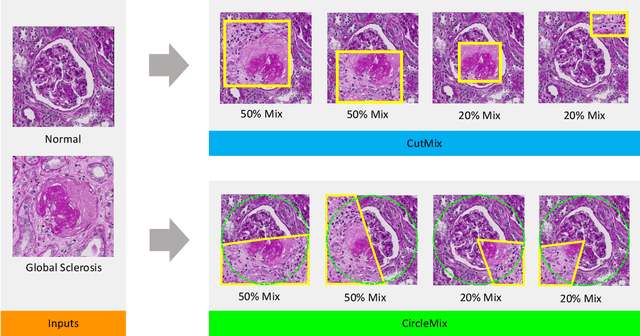
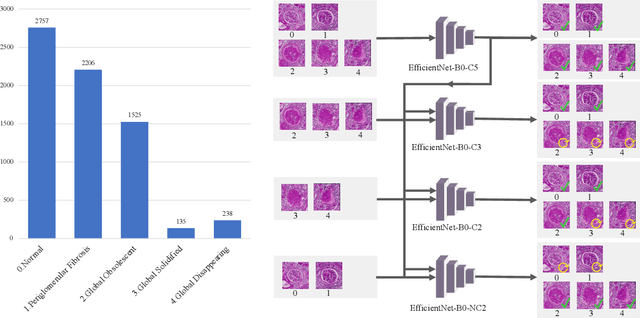
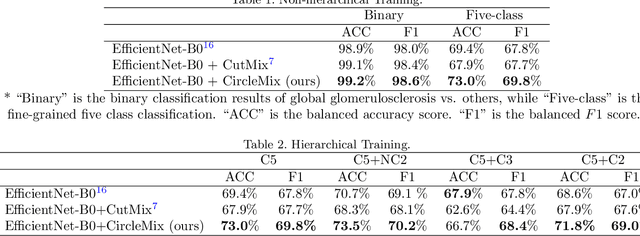
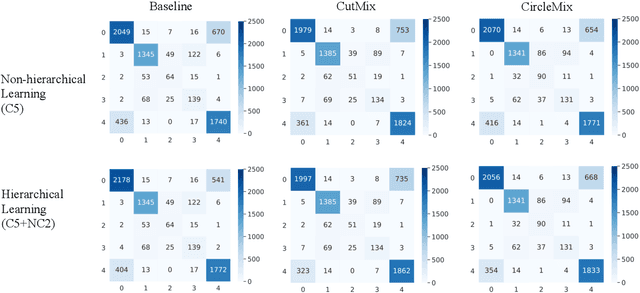
The classification of glomerular lesions is a routine and essential task in renal pathology. Recently, machine learning approaches, especially deep learning algorithms, have been used to perform computer-aided lesion characterization of glomeruli. However, one major challenge of developing such methods is the naturally imbalanced distribution of different lesions. In this paper, we propose CircleMix, a novel data augmentation technique, to improve the accuracy of classifying globally sclerotic glomeruli with a hierarchical learning strategy. Different from the recently proposed CutMix method, the CircleMix augmentation is optimized for the ball-shaped biomedical objects, such as glomeruli. 6,861 glomeruli with five classes (normal, periglomerular fibrosis, obsolescent glomerulosclerosis, solidified glomerulosclerosis, and disappearing glomerulosclerosis) were employed to develop and evaluate the proposed methods. From five-fold cross-validation, the proposed CircleMix augmentation achieved superior performance (Balanced Accuracy=73.0%) compared with the EfficientNet-B0 baseline (Balanced Accuracy=69.4%)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge