Implicit Neural Representations for Robust Joint Sparse-View CT Reconstruction
Paper and Code
May 03, 2024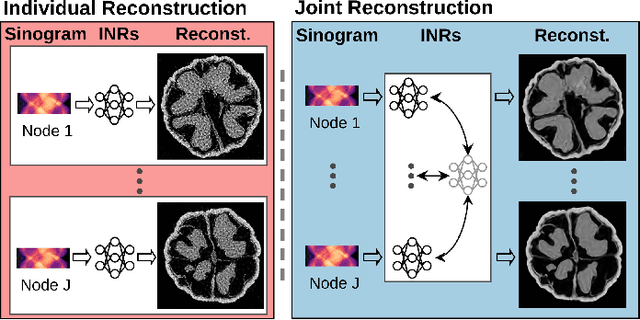
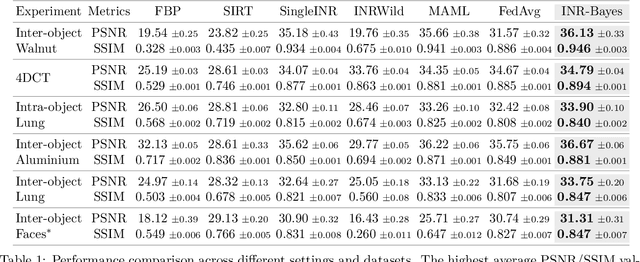
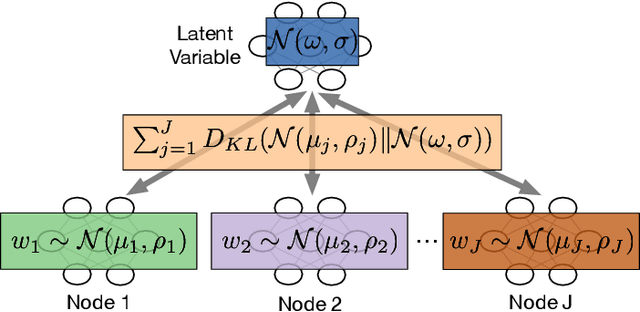
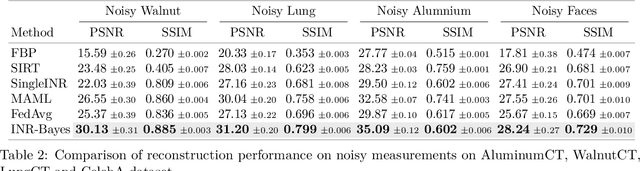
Computed Tomography (CT) is pivotal in industrial quality control and medical diagnostics. Sparse-view CT, offering reduced ionizing radiation, faces challenges due to its under-sampled nature, leading to ill-posed reconstruction problems. Recent advancements in Implicit Neural Representations (INRs) have shown promise in addressing sparse-view CT reconstruction. Recognizing that CT often involves scanning similar subjects, we propose a novel approach to improve reconstruction quality through joint reconstruction of multiple objects using INRs. This approach can potentially leverage both the strengths of INRs and the statistical regularities across multiple objects. While current INR joint reconstruction techniques primarily focus on accelerating convergence via meta-initialization, they are not specifically tailored to enhance reconstruction quality. To address this gap, we introduce a novel INR-based Bayesian framework integrating latent variables to capture the inter-object relationships. These variables serve as a dynamic reference throughout the optimization, thereby enhancing individual reconstruction fidelity. Our extensive experiments, which assess various key factors such as reconstruction quality, resistance to overfitting, and generalizability, demonstrate significant improvements over baselines in common numerical metrics. This underscores a notable advancement in CT reconstruction methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge