Impact of Adversarial Training on Robustness and Generalizability of Language Models
Paper and Code
Nov 10, 2022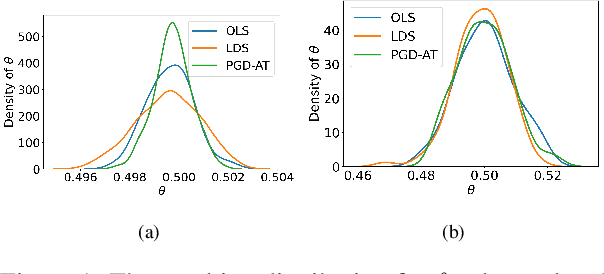
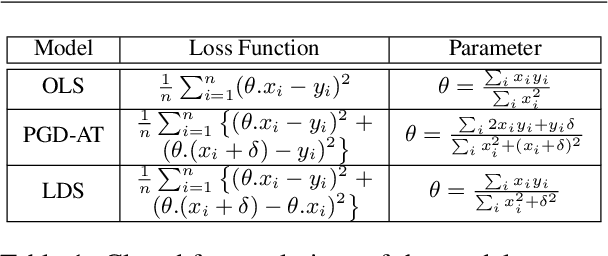
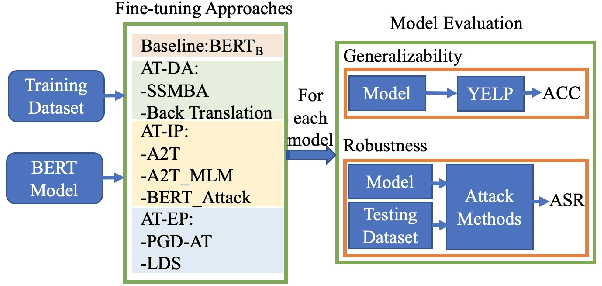
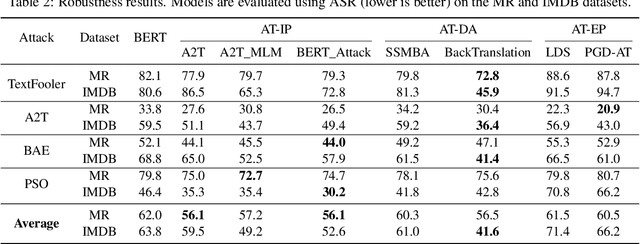
Adversarial training is widely acknowledged as the most effective defense against adversarial attacks. However, it is also well established that achieving both robustness and generalization in adversarially trained models involves a trade-off. The goal of this work is to provide an in depth comparison of different approaches for adversarial training in language models. Specifically, we study the effect of pre-training data augmentation as well as training time input perturbations vs. embedding space perturbations on the robustness and generalization of BERT-like language models. Our findings suggest that better robustness can be achieved by pre-training data augmentation or by training with input space perturbation. However, training with embedding space perturbation significantly improves generalization. A linguistic correlation analysis of neurons of the learned models reveal that the improved generalization is due to `more specialized' neurons. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to carry out a deep qualitative analysis of different methods of generating adversarial examples in adversarial training of language models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge