Impact Makes a Sound and Sound Makes an Impact: Sound Guides Representations and Explorations
Paper and Code
Aug 04, 2022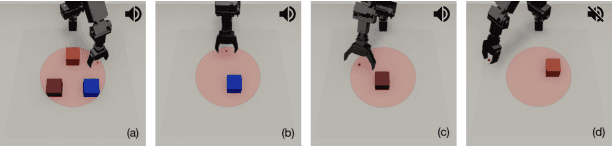
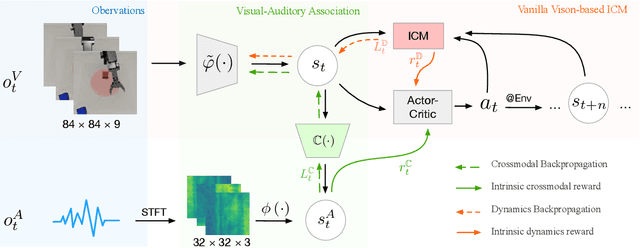
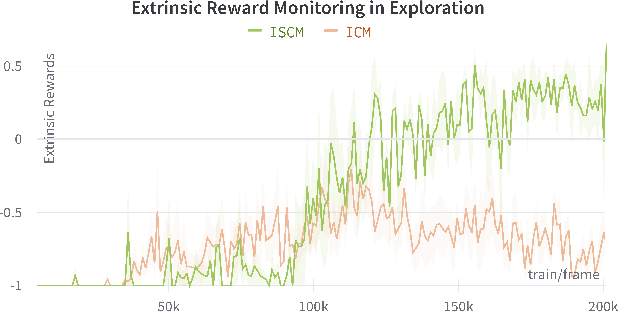
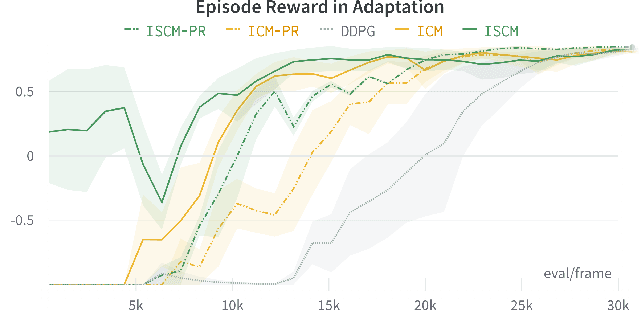
Sound is one of the most informative and abundant modalities in the real world while being robust to sense without contacts by small and cheap sensors that can be placed on mobile devices. Although deep learning is capable of extracting information from multiple sensory inputs, there has been little use of sound for the control and learning of robotic actions. For unsupervised reinforcement learning, an agent is expected to actively collect experiences and jointly learn representations and policies in a self-supervised way. We build realistic robotic manipulation scenarios with physics-based sound simulation and propose the Intrinsic Sound Curiosity Module (ISCM). The ISCM provides feedback to a reinforcement learner to learn robust representations and to reward a more efficient exploration behavior. We perform experiments with sound enabled during pre-training and disabled during adaptation, and show that representations learned by ISCM outperform the ones by vision-only baselines and pre-trained policies can accelerate the learning process when applied to downstream tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge