Image Restoration with Point Spread Function Regularization and Active Learning
Paper and Code
Oct 31, 2023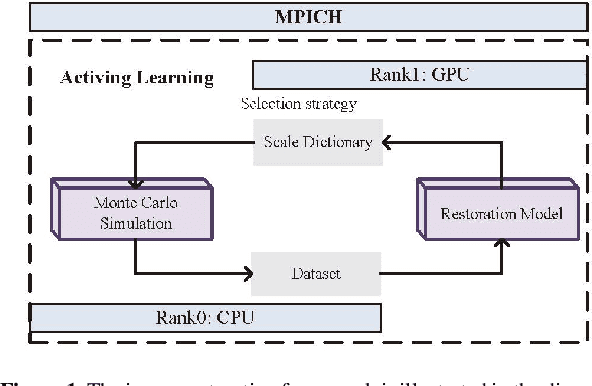
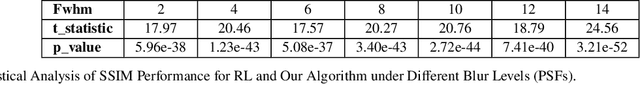

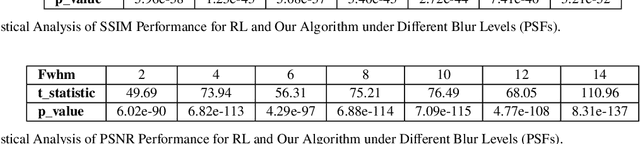
Large-scale astronomical surveys can capture numerous images of celestial objects, including galaxies and nebulae. Analysing and processing these images can reveal intricate internal structures of these objects, allowing researchers to conduct comprehensive studies on their morphology, evolution, and physical properties. However, varying noise levels and point spread functions can hamper the accuracy and efficiency of information extraction from these images. To mitigate these effects, we propose a novel image restoration algorithm that connects a deep learning-based restoration algorithm with a high-fidelity telescope simulator. During the training stage, the simulator generates images with different levels of blur and noise to train the neural network based on the quality of restored images. After training, the neural network can directly restore images obtained by the telescope, as represented by the simulator. We have tested the algorithm using real and simulated observation data and have found that it effectively enhances fine structures in blurry images and increases the quality of observation images. This algorithm can be applied to large-scale sky survey data, such as data obtained by LSST, Euclid, and CSST, to further improve the accuracy and efficiency of information extraction, promoting advances in the field of astronomical research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge