iFlipper: Label Flipping for Individual Fairness
Paper and Code
Sep 15, 2022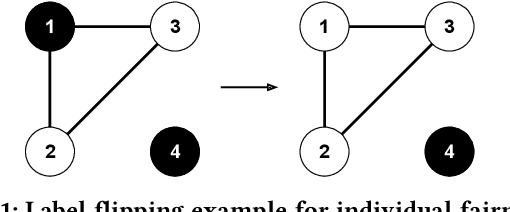
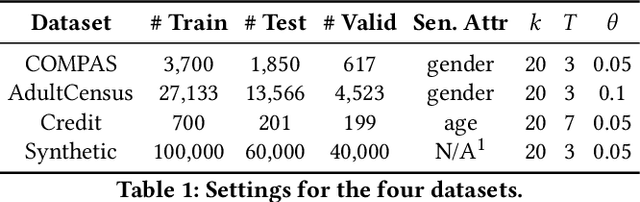
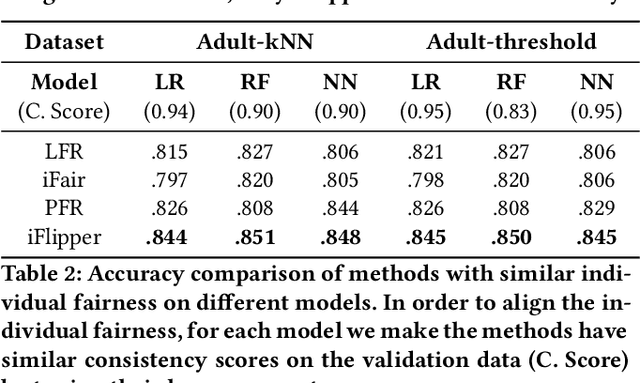
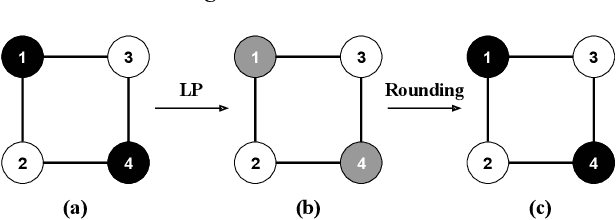
As machine learning becomes prevalent, mitigating any unfairness present in the training data becomes critical. Among the various notions of fairness, this paper focuses on the well-known individual fairness, which states that similar individuals should be treated similarly. While individual fairness can be improved when training a model (in-processing), we contend that fixing the data before model training (pre-processing) is a more fundamental solution. In particular, we show that label flipping is an effective pre-processing technique for improving individual fairness. Our system iFlipper solves the optimization problem of minimally flipping labels given a limit to the individual fairness violations, where a violation occurs when two similar examples in the training data have different labels. We first prove that the problem is NP-hard. We then propose an approximate linear programming algorithm and provide theoretical guarantees on how close its result is to the optimal solution in terms of the number of label flips. We also propose techniques for making the linear programming solution more optimal without exceeding the violations limit. Experiments on real datasets show that iFlipper significantly outperforms other pre-processing baselines in terms of individual fairness and accuracy on unseen test sets. In addition, iFlipper can be combined with in-processing techniques for even better results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge