I-ODA, Real-World Multi-modal Longitudinal Data for OphthalmicApplications
Paper and Code
Mar 30, 2021
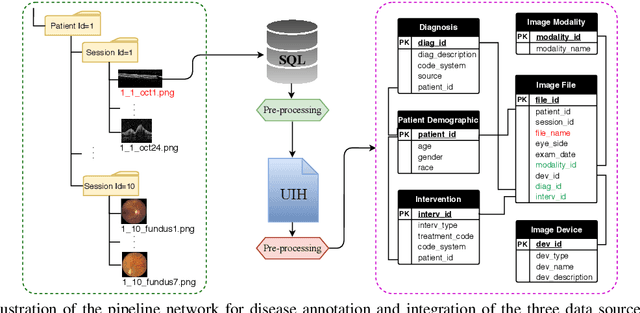
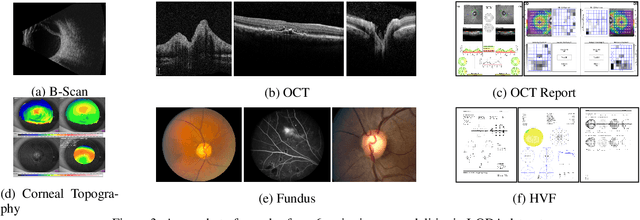
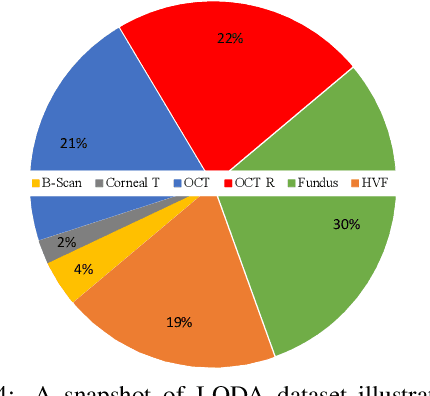
Data from clinical real-world settings is characterized by variability in quality, machine-type, setting, and source. One of the primary goals of medical computer vision is to develop and validate artificial intelligence (AI) based algorithms on real-world data enabling clinical translations. However, despite the exponential growth in AI based applications in healthcare, specifically in ophthalmology, translations to clinical settings remain challenging. Limited access to adequate and diverse real-world data inhibits the development and validation of translatable algorithms. In this paper, we present a new multi-modal longitudinal ophthalmic imaging dataset, the Illinois Ophthalmic Database Atlas (I-ODA), with the goal of advancing state-of-the-art computer vision applications in ophthalmology, and improving upon the translatable capacity of AI based applications across different clinical settings. We present the infrastructure employed to collect, annotate, and anonymize images from multiple sources, demonstrating the complexity of real-world retrospective data and its limitations. I-ODA includes 12 imaging modalities with a total of 3,668,649 ophthalmic images of 33,876 individuals from the Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences at the Illinois Eye and Ear Infirmary of the University of Illinois Chicago (UIC) over the course of 12 years.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge