Hyperspectral Image Classification with Deep Metric Learning and Conditional Random Field
Paper and Code
Mar 04, 2019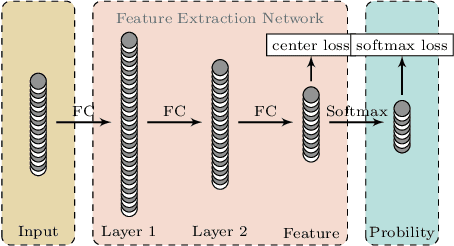
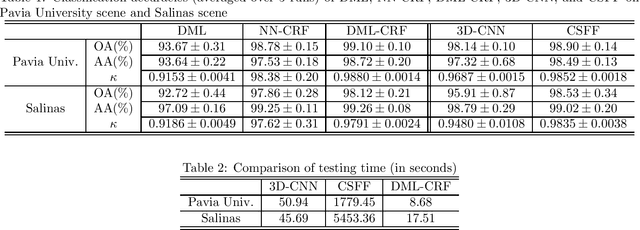
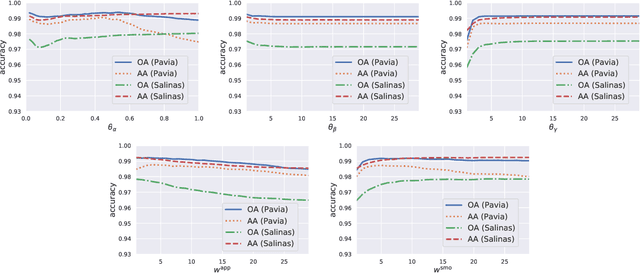

To improve the classification performance in the context of hyperspectral image processing, many works have been developed based on two common strategies, namely the spatial-spectral information integration and the utilization of neural networks. However, both strategies typically require more training data than the classical algorithms, aggregating the shortage of labeled samples. In this paper, we propose a novel framework that organically combines an existing spectrum-based deep metric learning model and the conditional random field algorithm. The deep metric learning model is supervised by center loss, and is used to produce spectrum-based features that gather more tightly within classes in Euclidean space. The conditional random field with Gaussian edge potentials, which is firstly proposed for image segmentation problem, is utilized to jointly account for both the geometry distance of two pixels and the Euclidean distance between their corresponding features extracted by the deep metric learning model. The final predictions are given by the conditional random field. Generally, the proposed framework is trained by spectra pixels at the deep metric learning stage, and utilizes the half handcrafted spatial features at the conditional random field stage. This settlement alleviates the shortage of training data to some extent. Experiments on two real hyperspectral images demonstrate the advantages of the proposed method in terms of both classification accuracy and computation cost.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge