Human-Inspired Audio-Visual Speech Recognition: Spike Activity, Cueing Interaction and Causal Processing
Paper and Code
Aug 29, 2024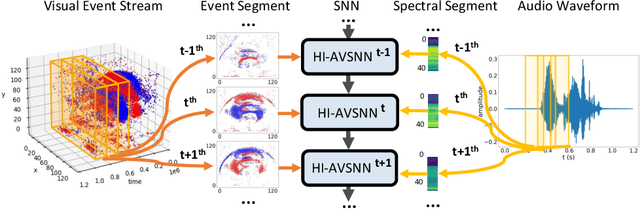
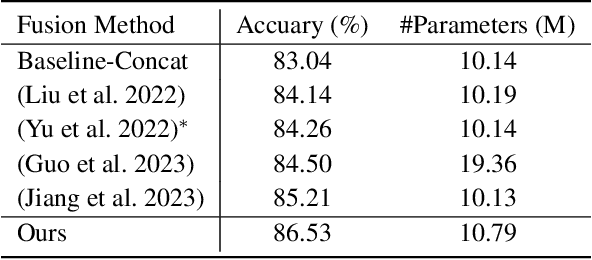
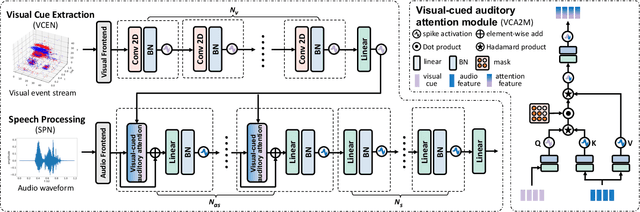
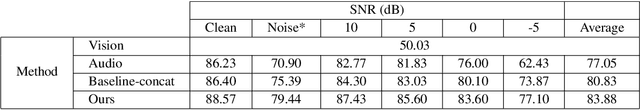
Humans naturally perform audiovisual speech recognition (AVSR), enhancing the accuracy and robustness by integrating auditory and visual information. Spiking neural networks (SNNs), which mimic the brain's information-processing mechanisms, are well-suited for emulating the human capability of AVSR. Despite their potential, research on SNNs for AVSR is scarce, with most existing audio-visual multimodal methods focused on object or digit recognition. These models simply integrate features from both modalities, neglecting their unique characteristics and interactions. Additionally, they often rely on future information for current processing, which increases recognition latency and limits real-time applicability. Inspired by human speech perception, this paper proposes a novel human-inspired SNN named HI-AVSNN for AVSR, incorporating three key characteristics: cueing interaction, causal processing and spike activity. For cueing interaction, we propose a visual-cued auditory attention module (VCA2M) that leverages visual cues to guide attention to auditory features. We achieve causal processing by aligning the SNN's temporal dimension with that of visual and auditory features and applying temporal masking to utilize only past and current information. To implement spike activity, in addition to using SNNs, we leverage the event camera to capture lip movement as spikes, mimicking the human retina and providing efficient visual data. We evaluate HI-AVSNN on an audiovisual speech recognition dataset combining the DVS-Lip dataset with its corresponding audio samples. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our proposed fusion method, outperforming existing audio-visual SNN fusion methods and achieving a 2.27% improvement in accuracy over the only existing SNN-based AVSR method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge