How Well Do LLMs Identify Cultural Unity in Diversity?
Paper and Code
Aug 09, 2024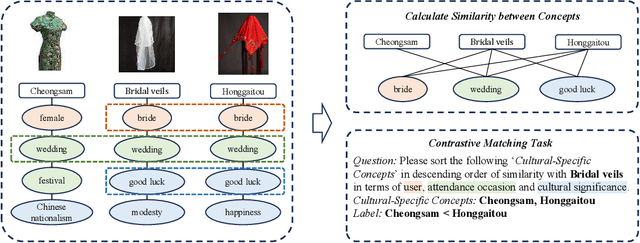

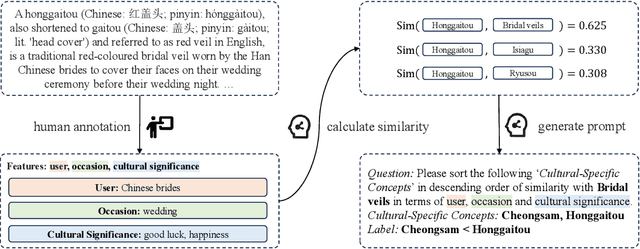
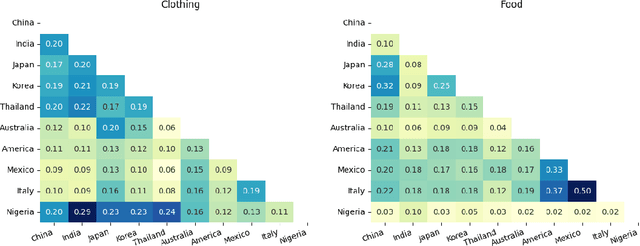
Much work on the cultural awareness of large language models (LLMs) focuses on the models' sensitivity to geo-cultural diversity. However, in addition to cross-cultural differences, there also exists common ground across cultures. For instance, a bridal veil in the United States plays a similar cultural-relevant role as a honggaitou in China. In this study, we introduce a benchmark dataset CUNIT for evaluating decoder-only LLMs in understanding the cultural unity of concepts. Specifically, CUNIT consists of 1,425 evaluation examples building upon 285 traditional cultural-specific concepts across 10 countries. Based on a systematic manual annotation of cultural-relevant features per concept, we calculate the cultural association between any pair of cross-cultural concepts. Built upon this dataset, we design a contrastive matching task to evaluate the LLMs' capability to identify highly associated cross-cultural concept pairs. We evaluate 3 strong LLMs, using 3 popular prompting strategies, under the settings of either giving all extracted concept features or no features at all on CUNIT Interestingly, we find that cultural associations across countries regarding clothing concepts largely differ from food. Our analysis shows that LLMs are still limited to capturing cross-cultural associations between concepts compared to humans. Moreover, geo-cultural proximity shows a weak influence on model performance in capturing cross-cultural associations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge