Heterogeneity Loss to Handle Intersubject and Intrasubject Variability in Cancer
Paper and Code
Mar 19, 2020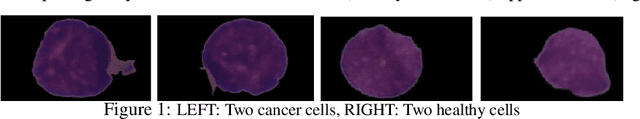

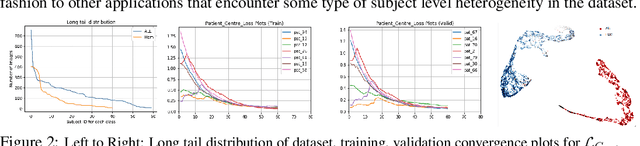
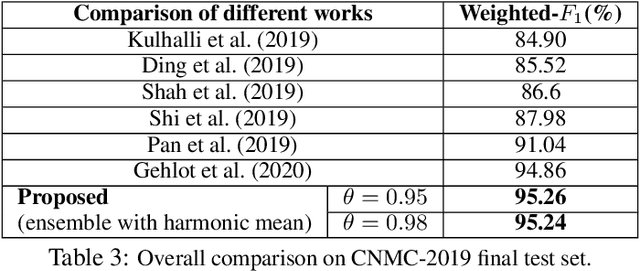
Developing nations lack adequate number of hospitals with modern equipment and skilled doctors. Hence, a significant proportion of these nations' population, particularly in rural areas, is not able to avail specialized and timely healthcare facilities. In recent years, deep learning (DL) models, a class of artificial intelligence (AI) methods, have shown impressive results in medical domain. These AI methods can provide immense support to developing nations as affordable healthcare solutions. This work is focused on one such application of blood cancer diagnosis. However, there are some challenges to DL models in cancer research because of the unavailability of a large data for adequate training and the difficulty of capturing heterogeneity in data at different levels ranging from acquisition characteristics, session, to subject-level (within subjects and across subjects). These challenges render DL models prone to overfitting and hence, models lack generalization on prospective subjects' data. In this work, we address these problems in the application of B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (B-ALL) diagnosis using deep learning. We propose heterogeneity loss that captures subject-level heterogeneity, thereby, forcing the neural network to learn subject-independent features. We also propose an unorthodox ensemble strategy that helps us in providing improved classification over models trained on 7-folds giving a weighted-$F_1$ score of 95.26% on unseen (test) subjects' data that are, so far, the best results on the C-NMC 2019 dataset for B-ALL classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge