Hearing Loss Detection from Facial Expressions in One-on-one Conversations
Paper and Code
Jan 17, 2024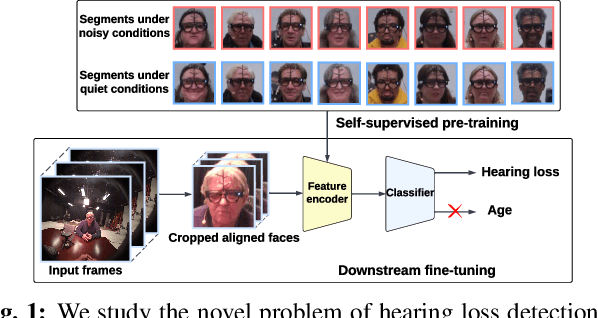
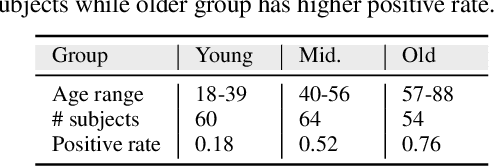
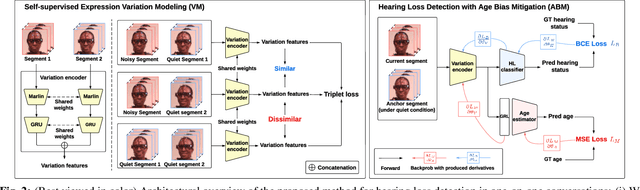
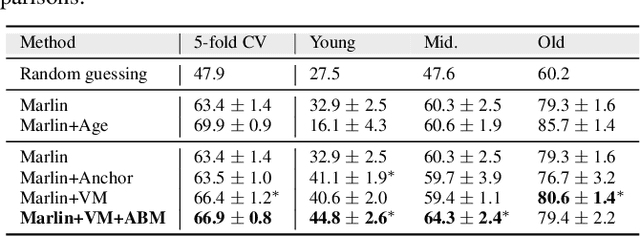
Individuals with impaired hearing experience difficulty in conversations, especially in noisy environments. This difficulty often manifests as a change in behavior and may be captured via facial expressions, such as the expression of discomfort or fatigue. In this work, we build on this idea and introduce the problem of detecting hearing loss from an individual's facial expressions during a conversation. Building machine learning models that can represent hearing-related facial expression changes is a challenge. In addition, models need to disentangle spurious age-related correlations from hearing-driven expressions. To this end, we propose a self-supervised pre-training strategy tailored for the modeling of expression variations. We also use adversarial representation learning to mitigate the age bias. We evaluate our approach on a large-scale egocentric dataset with real-world conversational scenarios involving subjects with hearing loss and show that our method for hearing loss detection achieves superior performance over baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge