HC3 Plus: A Semantic-Invariant Human ChatGPT Comparison Corpus
Paper and Code
Sep 06, 2023
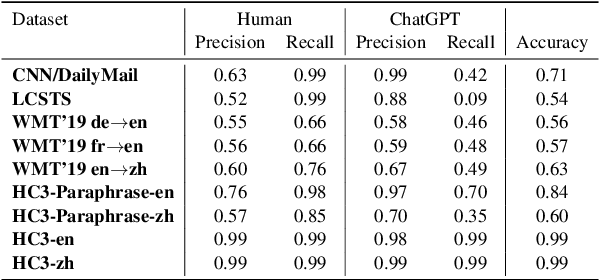
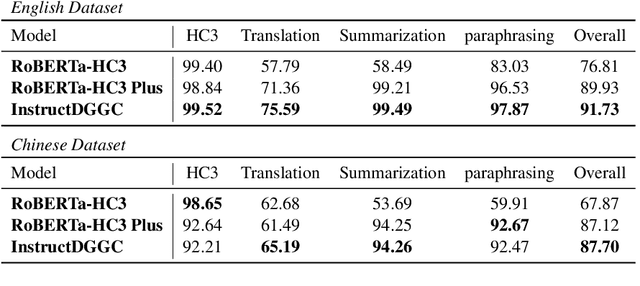

ChatGPT has gained significant interest due to its impressive performance, but people are increasingly concerned about its potential risks, particularly around the detection of AI-generated content (AIGC), which is often difficult for untrained humans to identify. Current datasets utilized for detecting ChatGPT-generated text primarily center around question-answering, yet they tend to disregard tasks that possess semantic-invariant properties, such as summarization, translation, and paraphrasing. Our primary studies demonstrate that detecting model-generated text on semantic-invariant tasks is more difficult. To fill this gap, we introduce a more extensive and comprehensive dataset that considers more types of tasks than previous work, including semantic-invariant tasks. In addition, the model after a large number of task instruction fine-tuning shows a strong powerful performance. Owing to its previous success, we further instruct fine-tuning Tk-instruct and built a more powerful detection system. Experimental results show that our proposed detector outperforms the previous state-of-the-art RoBERTa-based detector.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge