HAWQ: Hessian AWare Quantization of Neural Networks with Mixed-Precision
Paper and Code
Apr 29, 2019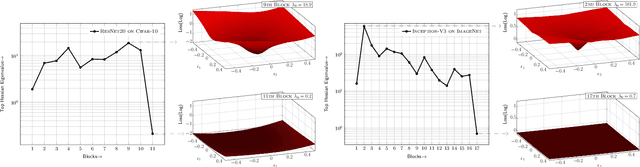
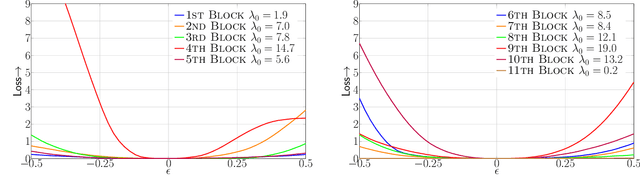
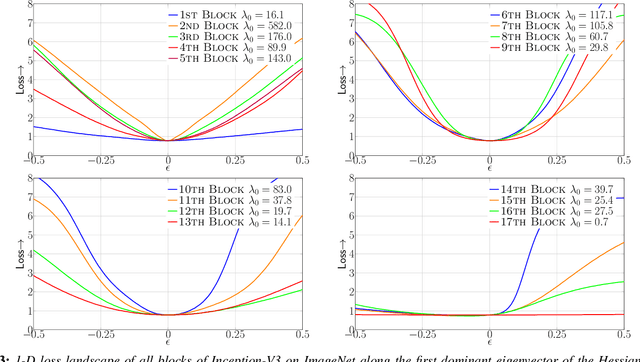
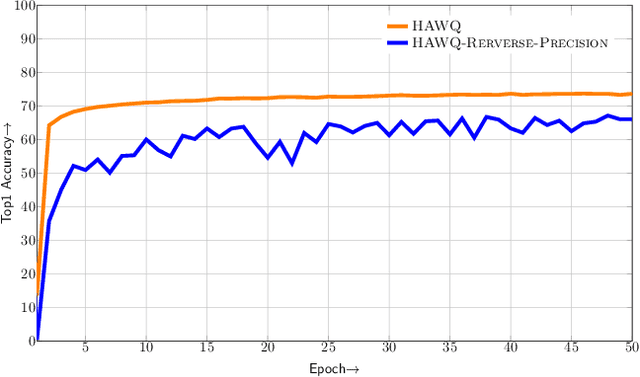
Model size and inference speed/power have become a major challenge in the deployment of Neural Networks for many applications. A promising approach to address these problems is quantization. However, uniformly quantizing a model to ultra low precision leads to significant accuracy degradation. A novel solution for this is to use mixed-precision quantization, as some parts of the network may allow lower precision as compared to other layers. However, there is no systematic way to determine the precision of different layers. A brute force approach is not feasible for deep networks, as the search space for mixed-precision is exponential in the number of layers. Another challenge is a similar factorial complexity for determining block-wise fine-tuning order when quantizing the model to a target precision. Here, we introduce Hessian AWare Quantization (HAWQ), a novel second-order quantization method to address these problems. HAWQ allows for the automatic selection of the relative quantization precision of each layer, based on the layer's Hessian spectrum. Moreover, HAWQ provides a deterministic fine-tuning order for quantizing layers, based on second-order information. We show the results of our method on Cifar-10 using ResNet20, and on ImageNet using Inception-V3, ResNet50 and SqueezeNext models. Comparing HAWQ with state-of-the-art shows that we can achieve similar/better accuracy with $8\times$ activation compression ratio on ResNet20, as compared to DNAS~\cite{wu2018mixed}, and up to $1\%$ higher accuracy with up to $14\%$ smaller models on ResNet50 and Inception-V3, compared to recently proposed methods of RVQuant~\cite{park2018value} and HAQ~\cite{wang2018haq}. Furthermore, we show that we can quantize SqueezeNext to just 1MB model size while achieving above $68\%$ top1 accuracy on ImageNet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge