Has Anything Changed? 3D Change Detection by 2D Segmentation Masks
Paper and Code
Dec 02, 2023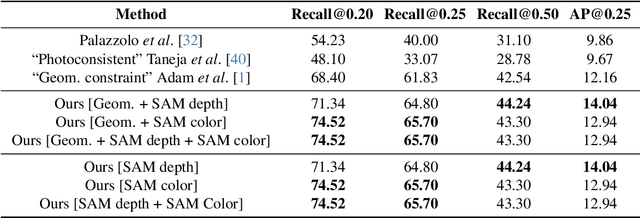
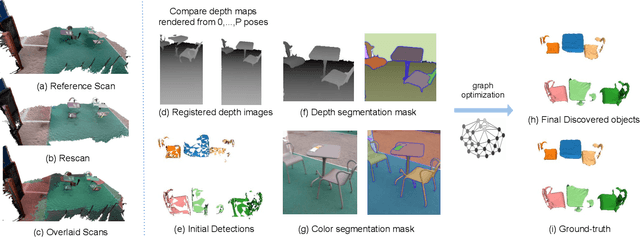
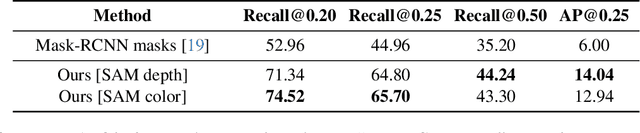
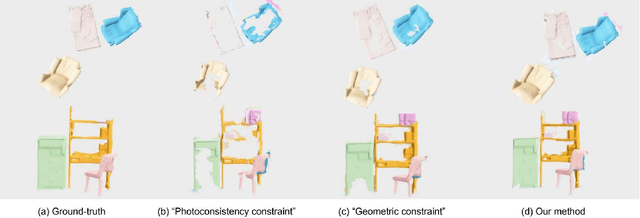
As capturing devices become common, 3D scans of interior spaces are acquired on a daily basis. Through scene comparison over time, information about objects in the scene and their changes is inferred. This information is important for robots and AR and VR devices, in order to operate in an immersive virtual experience. We thus propose an unsupervised object discovery method that identifies added, moved, or removed objects without any prior knowledge of what objects exist in the scene. We model this problem as a combination of a 3D change detection and a 2D segmentation task. Our algorithm leverages generic 2D segmentation masks to refine an initial but incomplete set of 3D change detections. The initial changes, acquired through render-and-compare likely correspond to movable objects. The incomplete detections are refined through graph optimization, distilling the information of the 2D segmentation masks in the 3D space. Experiments on the 3Rscan dataset prove that our method outperforms competitive baselines, with SoTA results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge