Guidance, Navigation and Control of Multirobot Systems in Cooperative Cliff Climbing
Paper and Code
Feb 21, 2017
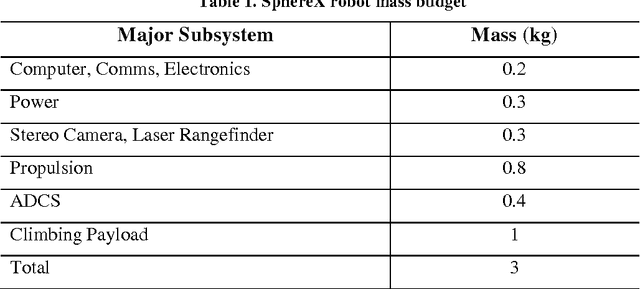


The application of GNC devices on small robots is a game-changer that enables these robots to be mobile on low-gravity planetary surfaces and small bodies. Use of reaction wheels enables these robots to roll, hop, summersault and rest on precarious/sloped surfaces that would otherwise not be possible with conven-tional wheeled robots. We are extending this technology to enable robots to climb off-world canyons, cliffs and caves. A single robot may slip and fall, however, a multirobot system can work cooperatively by being interlinked using spring-tethers and work much like a team of mountaineers to systematically climb a slope. A multirobot system as we will show in this paper can climb sur-faces not possible with a single robot alone. We consider a team of four robots that are interlinked with tethers in an 'x' configuration. Each robot secures itself to a slope using spiny gripping actuators, and one by one each robot moves up-wards by crawling, rolling or hopping up the slope. If any one of the robots loses grip, slips or falls, the remaining robots will be holding it up as they are anchored. This distributed controls approach to cliff climbing enables the system to reconfigure itself where possible and avoid getting stuck at one hard to reach location. Instead, the risk is distributed and through close cooperation, the robots can identify multiple trajectories to climb a cliff or rugged surface. The benefits can also be realized on milligravity surfaces such as asteroids. Too fast a jump can result in the robot flying off the surface into space. Having multiple robots anchored to the surface keeps the entire system secure. Our work combines dynamics and control simulation to evaluate the feasibility of our approach. The simulation results show a promising pathway towards advanced development of this technology on a team of real robots.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge