Graphs Generalization under Distribution Shifts
Paper and Code
Mar 25, 2024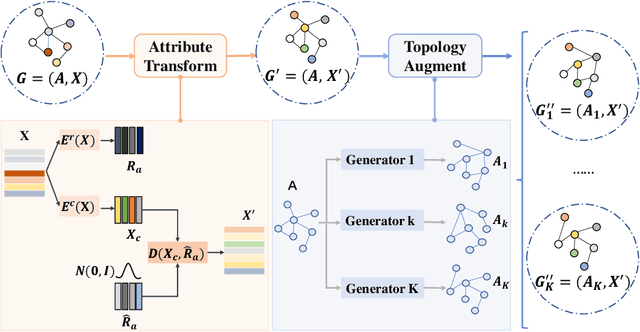
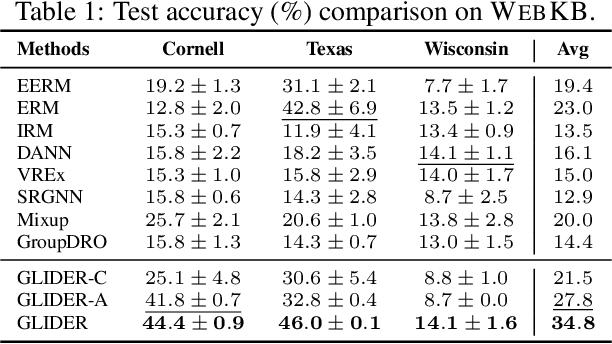
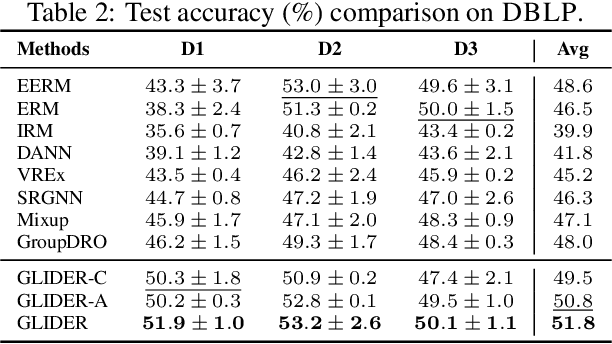
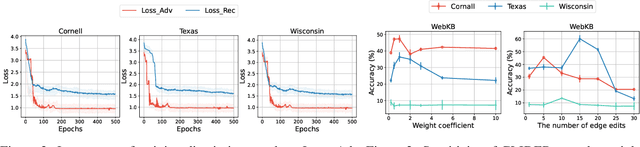
Traditional machine learning methods heavily rely on the independent and identically distribution assumption, which imposes limitations when the test distribution deviates from the training distribution. To address this crucial issue, out-of-distribution (OOD) generalization, which aims to achieve satisfactory generalization performance when faced with unknown distribution shifts, has made a significant process. However, the OOD method for graph-structured data currently lacks clarity and remains relatively unexplored due to two primary challenges. Firstly, distribution shifts on graphs often occur simultaneously on node attributes and graph topology. Secondly, capturing invariant information amidst diverse distribution shifts proves to be a formidable challenge. To overcome these obstacles, in this paper, we introduce a novel framework, namely Graph Learning Invariant Domain genERation (GLIDER). The goal is to (1) diversify variations across domains by modeling the potential seen or unseen variations of attribute distribution and topological structure and (2) minimize the discrepancy of the variation in a representation space where the target is to predict semantic labels. Extensive experiment results indicate that our model outperforms baseline methods on node-level OOD generalization across domains in distribution shift on node features and topological structures simultaneously.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge