Graph-Fraudster: Adversarial Attacks on Graph Neural Network Based Vertical Federated Learning
Paper and Code
Oct 13, 2021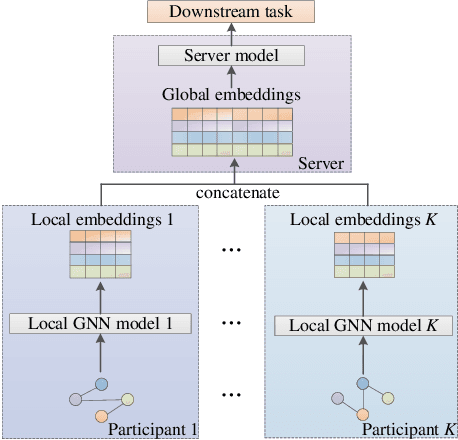
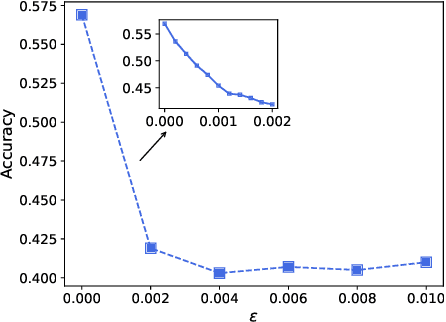
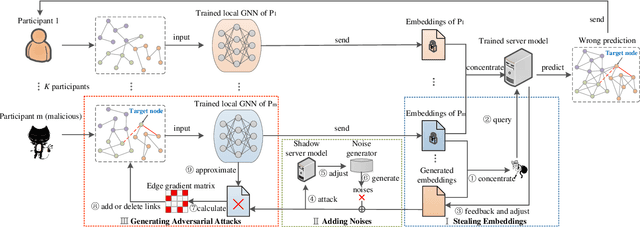
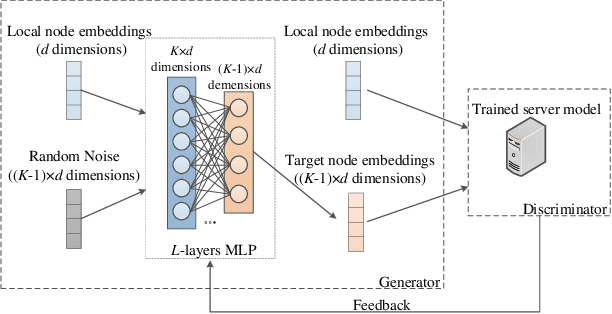
Graph neural network (GNN) models have achieved great success on graph representation learning. Challenged by large scale private data collection from user-side, GNN models may not be able to reflect the excellent performance, without rich features and complete adjacent relationships. Addressing to the problem, vertical federated learning (VFL) is proposed to implement local data protection through training a global model collaboratively. Consequently, for graph-structured data, it is natural idea to construct VFL framework with GNN models. However, GNN models are proven to be vulnerable to adversarial attacks. Whether the vulnerability will be brought into the VFL has not been studied. In this paper, we devote to study the security issues of GNN based VFL (GVFL), i.e., robustness against adversarial attacks. Further, we propose an adversarial attack method, named Graph-Fraudster. It generates adversarial perturbations based on the noise-added global node embeddings via GVFL's privacy leakage, and the gradient of pairwise node. First, it steals the global node embeddings and sets up a shadow server model for attack generator. Second, noises are added into node embeddings to confuse the shadow server model. At last, the gradient of pairwise node is used to generate attacks with the guidance of noise-added node embeddings. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study of adversarial attacks on GVFL. The extensive experiments on five benchmark datasets demonstrate that Graph-Fraudster performs better than three possible baselines in GVFL. Furthermore, Graph-Fraudster can remain a threat to GVFL even if two possible defense mechanisms are applied. This paper reveals that GVFL is vulnerable to adversarial attack similar to centralized GNN models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge