Generative Flows with Invertible Attentions
Paper and Code
Jun 26, 2021
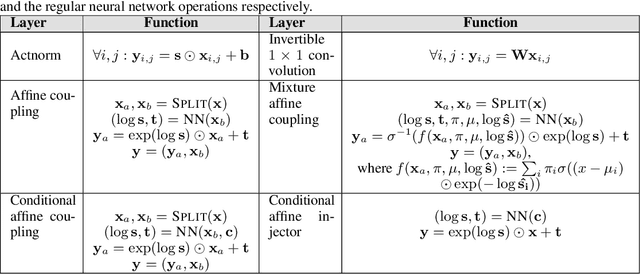


Flow-based generative models have shown excellent ability to explicitly learn the probability density function of data via a sequence of invertible transformations. Yet, modeling long-range dependencies over normalizing flows remains understudied. To fill the gap, in this paper, we introduce two types of invertible attention mechanisms for generative flow models. To be precise, we propose map-based and scaled dot-product attention for unconditional and conditional generative flow models. The key idea is to exploit split-based attention mechanisms to learn the attention weights and input representations on every two splits of flow feature maps. Our method provides invertible attention modules with tractable Jacobian determinants, enabling seamless integration of it at any positions of the flow-based models. The proposed attention mechanism can model the global data dependencies, leading to more comprehensive flow models. Evaluation on multiple generation tasks demonstrates that the introduced attention flow idea results in efficient flow models and compares favorably against the state-of-the-art unconditional and conditional generative flow methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge