Generalizable Person Re-Identification via Self-Supervised Batch Norm Test-Time Adaption
Paper and Code
Mar 28, 2022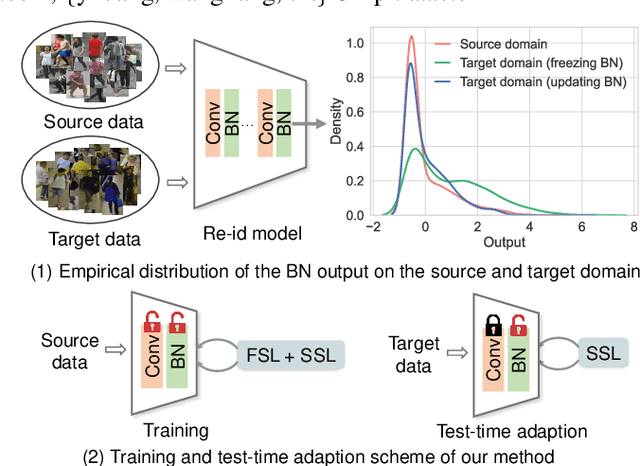
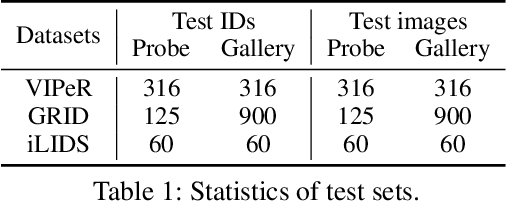
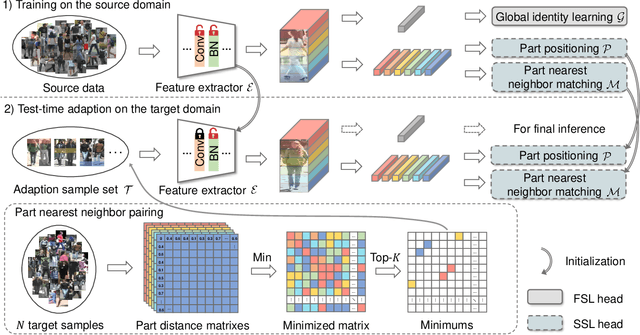
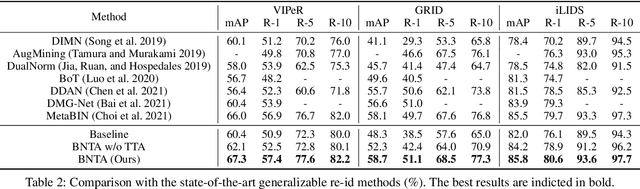
In this paper, we investigate the generalization problem of person re-identification (re-id), whose major challenge is the distribution shift on an unseen domain. As an important tool of regularizing the distribution, batch normalization (BN) has been widely used in existing methods. However, they neglect that BN is severely biased to the training domain and inevitably suffers the performance drop if directly generalized without being updated. To tackle this issue, we propose Batch Norm Test-time Adaption (BNTA), a novel re-id framework that applies the self-supervised strategy to update BN parameters adaptively. Specifically, BNTA quickly explores the domain-aware information within unlabeled target data before inference, and accordingly modulates the feature distribution normalized by BN to adapt to the target domain. This is accomplished by two designed self-supervised auxiliary tasks, namely part positioning and part nearest neighbor matching, which help the model mine the domain-aware information with respect to the structure and identity of body parts, respectively. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, we conduct extensive experiments on three re-id datasets and confirm the superior performance to the state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge