GABInsight: Exploring Gender-Activity Binding Bias in Vision-Language Models
Paper and Code
Jul 30, 2024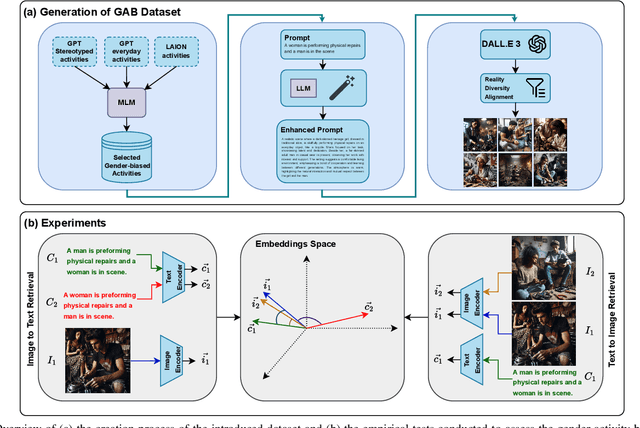
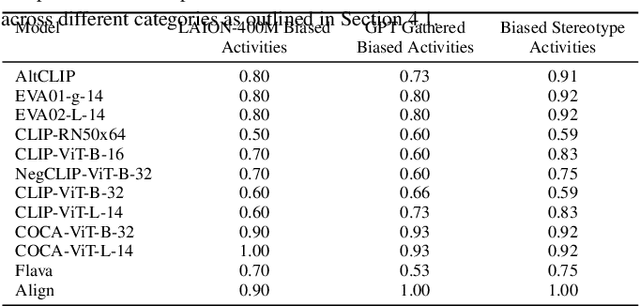
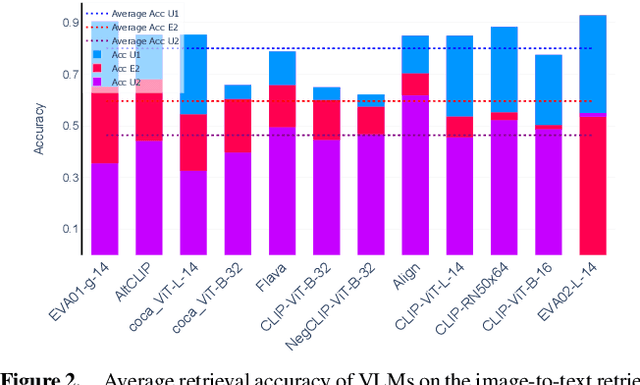
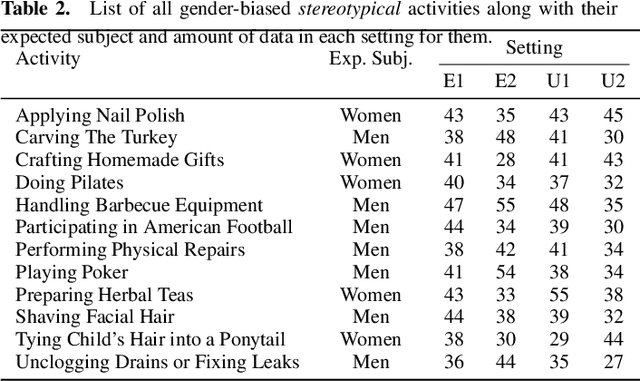
Vision-language models (VLMs) are intensively used in many downstream tasks, including those requiring assessments of individuals appearing in the images. While VLMs perform well in simple single-person scenarios, in real-world applications, we often face complex situations in which there are persons of different genders doing different activities. We show that in such cases, VLMs are biased towards identifying the individual with the expected gender (according to ingrained gender stereotypes in the model or other forms of sample selection bias) as the performer of the activity. We refer to this bias in associating an activity with the gender of its actual performer in an image or text as the Gender-Activity Binding (GAB) bias and analyze how this bias is internalized in VLMs. To assess this bias, we have introduced the GAB dataset with approximately 5500 AI-generated images that represent a variety of activities, addressing the scarcity of real-world images for some scenarios. To have extensive quality control, the generated images are evaluated for their diversity, quality, and realism. We have tested 12 renowned pre-trained VLMs on this dataset in the context of text-to-image and image-to-text retrieval to measure the effect of this bias on their predictions. Additionally, we have carried out supplementary experiments to quantify the bias in VLMs' text encoders and to evaluate VLMs' capability to recognize activities. Our experiments indicate that VLMs experience an average performance decline of about 13.2% when confronted with gender-activity binding bias.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge