From the Lab to the Desert: Fast Prototyping and Learning of Robot Locomotion
Paper and Code
Jun 06, 2017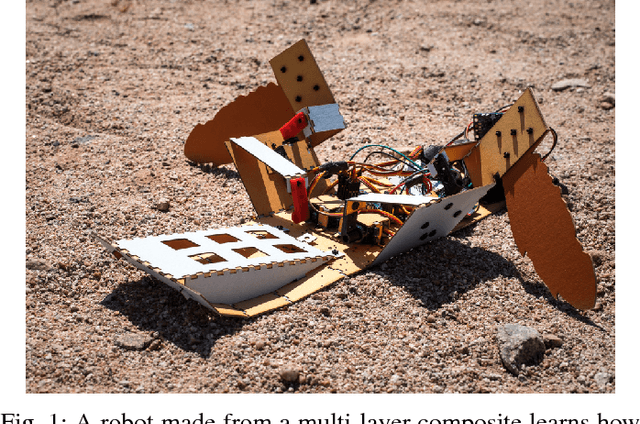
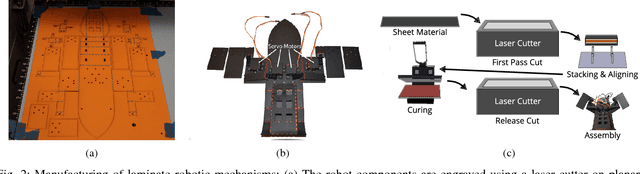

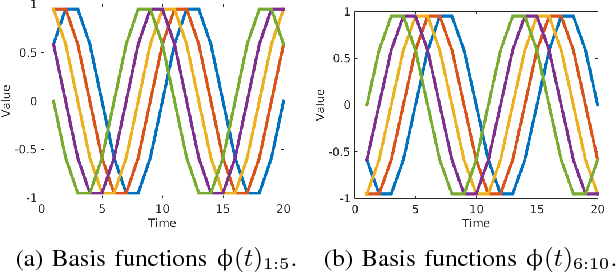
We present a methodology for fast prototyping of morphologies and controllers for robot locomotion. Going beyond simulation-based approaches, we argue that the form and function of a robot, as well as their interplay with real-world environmental conditions are critical. Hence, fast design and learning cycles are necessary to adapt robot shape and behavior to their environment. To this end, we present a combination of laminate robot manufacturing and sample-efficient reinforcement learning. We leverage this methodology to conduct an extensive robot learning experiment. Inspired by locomotion in sea turtles, we design a low-cost crawling robot with variable, interchangeable fins. Learning is performed using both bio-inspired and original fin designs in an artificial indoor environment as well as a natural environment in the Arizona desert. The findings of this study show that static policies developed in the laboratory do not translate to effective locomotion strategies in natural environments. In contrast to that, sample-efficient reinforcement learning can help to rapidly accommodate changes in the environment or the robot.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge