From molecules to scaffolds to functional groups: building context-dependent molecular representation via multi-channel learning
Paper and Code
Nov 05, 2023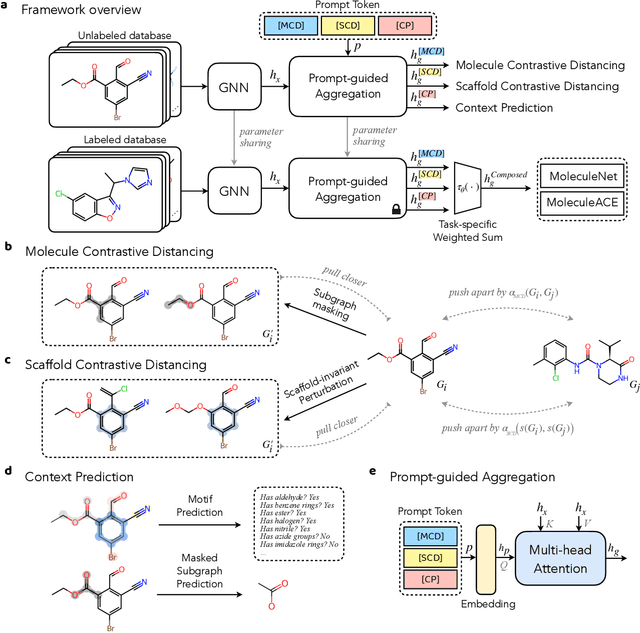
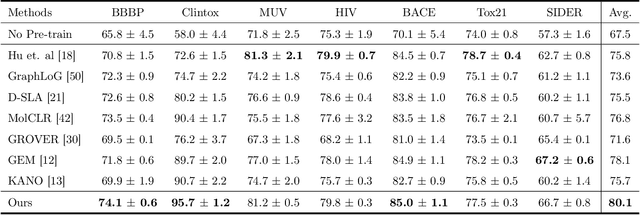
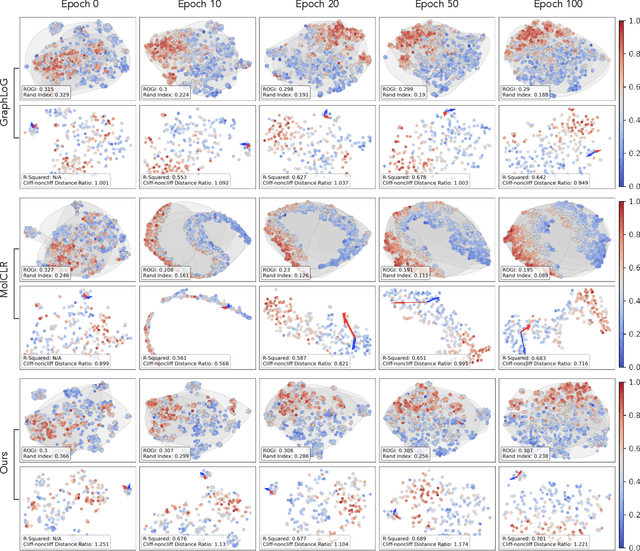

Reliable molecular property prediction is essential for various scientific endeavors and industrial applications, such as drug discovery. However, the scarcity of data, combined with the highly non-linear causal relationships between physicochemical and biological properties and conventional molecular featurization schemes, complicates the development of robust molecular machine learning models. Self-supervised learning (SSL) has emerged as a popular solution, utilizing large-scale, unannotated molecular data to learn a foundational representation of chemical space that might be advantageous for downstream tasks. Yet, existing molecular SSL methods largely overlook domain-specific knowledge, such as molecular similarity and scaffold importance, as well as the context of the target application when operating over the large chemical space. This paper introduces a novel learning framework that leverages the knowledge of structural hierarchies within molecular structures, embeds them through separate pre-training tasks over distinct channels, and employs a task-specific channel selection to compose a context-dependent representation. Our approach demonstrates competitive performance across various molecular property benchmarks and establishes some state-of-the-art results. It further offers unprecedented advantages in particularly challenging yet ubiquitous scenarios like activity cliffs with enhanced robustness and generalizability compared to other baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge