Free Lunch for Generating Effective Outlier Supervision
Paper and Code
Jan 17, 2023
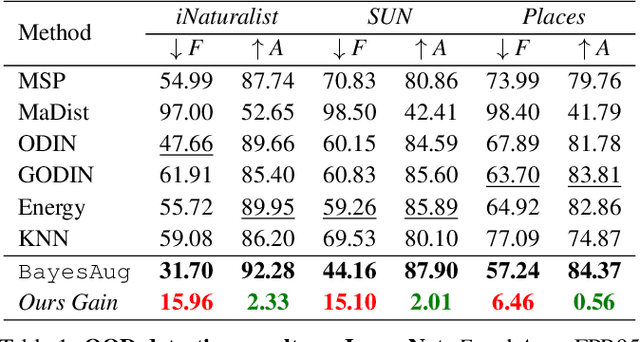
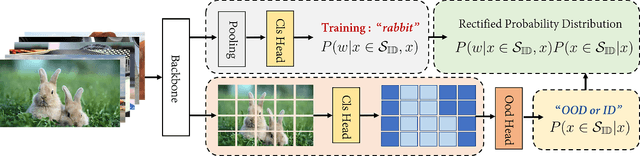
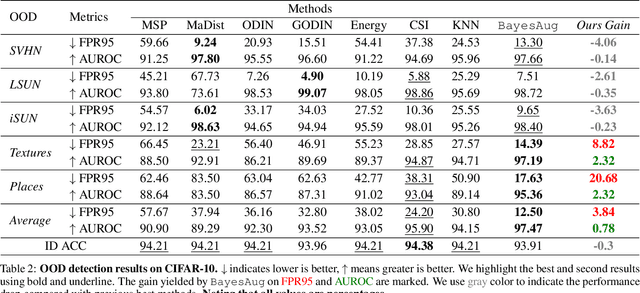
When deployed in practical applications, computer vision systems will encounter numerous unexpected images (\emph{{i.e.}}, out-of-distribution data). Due to the potentially raised safety risks, these aforementioned unseen data should be carefully identified and handled. Generally, existing approaches in dealing with out-of-distribution (OOD) detection mainly focus on the statistical difference between the features of OOD and in-distribution (ID) data extracted by the classifiers. Although many of these schemes have brought considerable performance improvements, reducing the false positive rate (FPR) when processing open-set images, they necessarily lack reliable theoretical analysis and generalization guarantees. Unlike the observed ways, in this paper, we investigate the OOD detection problem based on the Bayes rule and present a convincing description of the reason for failures encountered by conventional classifiers. Concretely, our analysis reveals that refining the probability distribution yielded by the vanilla neural networks is necessary for OOD detection, alleviating the issues of assigning high confidence to OOD data. To achieve this effortlessly, we propose an ultra-effective method to generate near-realistic outlier supervision. Extensive experiments on large-scale benchmarks reveal that our proposed \texttt{BayesAug} significantly reduces the FPR95 over 12.50\% compared with the previous schemes, boosting the reliability of machine learning systems. The code will be made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge